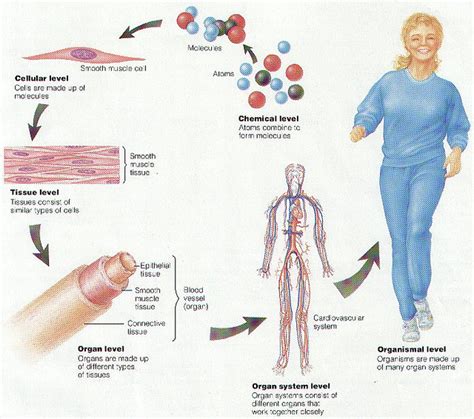
Human physiology is the study of the structure and function of the human body. It is a complex and demanding subject that requires a strong understanding of anatomy, biochemistry, and physics. Physiology courses typically cover a wide range of topics, including:

- The cardiovascular system
- The respiratory system
- The nervous system
- The endocrine system
- The digestive system
- The urinary system
- The reproductive system
Physiology is a challenging subject, but it is also essential for understanding how the human body works. A strong understanding of physiology is necessary for a variety of careers in the healthcare field, including medicine, nursing, and physical therapy.
The Challenges of Human Physiology Coursework
There are a number of challenges associated with human physiology coursework. One of the biggest challenges is the sheer volume of material that must be covered. Physiology is a complex subject, and there is a lot of information that students need to learn. This can be overwhelming for some students, and it can be difficult to keep up with the pace of the course.
Another challenge of physiology coursework is the level of detail that is required. Physiology is a very precise subject, and students need to be able to understand the details of how the human body works. This can be difficult for some students, especially those who are not used to thinking in a scientific way.
Finally, physiology coursework can be very demanding in terms of time and effort. Physiology is a laboratory-based science, and students need to spend a significant amount of time in the lab conducting experiments. This can be time-consuming, and it can be difficult to balance the demands of physiology coursework with other academic and personal commitments.
Strategies for Success in Human Physiology Coursework
There are a number of strategies that students can use to succeed in human physiology coursework. One important strategy is to start studying early. Physiology is a complex subject, and it is important to give yourself plenty of time to learn the material. Another important strategy is to be organized. Keep a notebook where you can keep track of your notes, assignments, and upcoming deadlines.
It is also important to make use of the resources that are available to you. Your instructor is a valuable resource, and they can provide you with guidance and support. Your classmates can also be a valuable resource. Form a study group and work together to learn the material.
Finally, it is important to be persistent. Physiology is a challenging subject, but it is possible to succeed if you are willing to put in the effort. Set realistic goals for yourself, and don’t give up if you don’t understand something right away. With hard work and dedication, you can succeed in human physiology coursework.
The Benefits of a Strong Understanding of Human Physiology
A strong understanding of human physiology can benefit you in a number of ways. First, it can help you to make healthier choices. By understanding how your body works, you can make better decisions about what to eat, how to exercise, and how to take care of yourself.
Second, a strong understanding of human physiology can help you to be a more informed patient. When you see your doctor, you will be able to ask better questions and make more informed decisions about your healthcare.
Third, a strong understanding of human physiology can help you to pursue a career in the healthcare field. Physiology is a required course for many healthcare professions, including medicine, nursing, and physical therapy. A strong understanding of physiology will give you a competitive advantage in the job market.
The following tables provide some useful information about human physiology:
| System | Organs | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular system | Heart, blood vessels, blood | Pump and transport blood throughout the body |
| Respiratory system | Lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles | Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the air |
| Nervous system | Brain, spinal cord, nerves | Control and coordinate the activities of the body |
| Endocrine system | Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas | Produce and secrete hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, growth, and development |
| Digestive system | Esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum | Digest food and absorb nutrients |
| Urinary system | Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra | Filter waste products from the blood and produce urine |
| Reproductive system | Ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes (female); testes, penis (male) | Produce and transport gametes (eggs and sperm) |