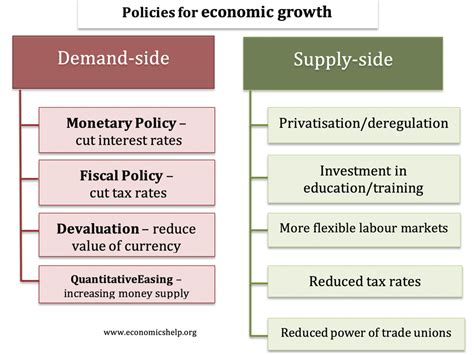
Economics, the study of the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, is a multifaceted field encompassing various areas of specialization. Economists, with their expertise in these different branches, play a pivotal role in shaping economic policies, analyzing market trends, and informing decision-making at various levels. Let’s delve into the diverse types of economists and their distinct contributions to the economic landscape:

1. Monetary Economists: Masters of Money and Interest Rates
Monetary economists are the custodians of a nation’s monetary system. They research the relationship between money, inflation, interest rates, and economic growth. These experts play a crucial role in formulating monetary policies that aim to stabilize prices, promote economic expansion, and manage inflation. Their insights help governments and central banks set appropriate interest rates and control the supply of money in circulation.
Figure 1: U.S. Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes, 2021-2023
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
2. Fiscal Economists: Architects of Government Spending and Taxation
Fiscal economists focus on the government’s role in the economy. They analyze the impact of taxes, government spending, and budget deficits on economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. Their expertise enables them to design fiscal policies that promote economic stability and efficiency. Fiscal economists also assess the effectiveness of government programs, providing valuable insights for policymakers.
Figure 2: U.S. Government Spending by Category, 2022
Source: Congressional Budget Office
3. Labor Economists: Champions of the Workforce
Labor economists delve into the dynamics of the labor market. They study issues such as employment, wages, job training, and labor unions. Their research helps policymakers address unemployment, promote job creation, and ensure fair labor practices. Labor economists also provide valuable insights into wage inequality, labor productivity, and the impact of technology on the workforce.
Figure 3: U.S. Unemployment Rate, 2010-2023
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
4. Development Economists: Catalysts for Economic Growth
Development economists focus on the economic challenges faced by developing countries. They analyze issues such as poverty reduction, economic inequality, and access to education and healthcare. Their expertise helps governments and international organizations design policies that promote sustainable economic growth, reduce poverty, and improve living standards in economically disadvantaged regions.
Figure 4: Global Poverty Rate, 1990-2022
Source: World Bank
5. International Economists: Navigating Global Economic Interconnections
International economists study the global economy and the interconnectedness of nations. They analyze issues such as international trade, foreign exchange rates, and the global financial system. Their expertise helps policymakers negotiate international trade agreements, promote economic cooperation, and manage global economic risks. International economists also provide insights into the impact of globalization on economies worldwide.
6. Health Economists: Optimizing Healthcare Delivery
Health economists apply economic principles to the healthcare sector. They analyze issues such as healthcare costs, access to healthcare, and the efficiency of healthcare systems. Their research helps policymakers design healthcare policies that improve access to affordable and quality healthcare for all. Health economists also evaluate the effectiveness of healthcare interventions and promote cost-effective treatments.
7. Environmental Economists: Guardians of Sustainable Development
Environmental economists focus on the relationship between the economy and the environment. They analyze the impact of economic activities on the environment and develop policies that promote sustainable development. Their research helps policymakers address issues such as climate change, pollution, and resource depletion. Environmental economists also work with businesses to develop eco-friendly technologies and practices.
8. Behavioral Economists: Understanding Human Decision-Making
Behavioral economists combine insights from economics and psychology to study human decision-making. They analyze how cognitive biases, emotions, and social interactions influence economic choices. Their research has implications for policy design, marketing strategies, and personal finance. Behavioral economists help policymakers understand why people make certain economic decisions and develop policies that nudge them towards more rational choices.
9. Experimental Economists: Testing Economic Theories in the Lab
Experimental economists use controlled experiments to test economic theories and hypotheses. They design experiments that simulate real-world economic scenarios and observe how subjects behave in these situations. Experimental economists provide strong evidence for economic models and help policymakers evaluate the effectiveness of different policies. They also contribute to the development of new economic theories.
Conclusion
The diverse field of economics encompasses a wide range of specializations, each contributing to our understanding of the economic system. From monetary economists shaping interest rates to development economists catalyzing economic growth, economists play a vital role in shaping economic policies, informing decision-making, and addressing the world’s most pressing economic challenges. As the world faces new economic challenges, the expertise and insights of economists will continue to be invaluable in navigating the complexities of the global economy and promoting sustainable and equitable economic growth for all.