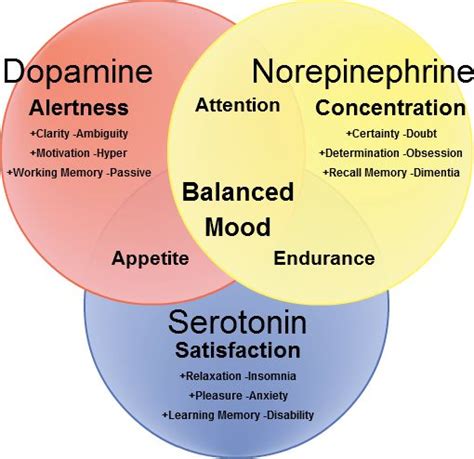
Introduction

In AP Psychology, dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in motivation, reward, learning, and attention. Understanding its functions and mechanisms is essential for comprehending the complex workings of the brain and behavior. This article explores the definition of dopamine in AP Psychology, delving into its role in various cognitive and behavioral processes.
Definition of Dopamine in AP Psychology
Dopamine, abbreviated as DA, is a catecholamine neurotransmitter synthesized in the brain’s substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area (VTA). It is primarily responsible for mediating the brain’s reward system, motivating us to pursue and engage in pleasurable activities. Dopamine signals are released when we experience rewards, such as food, money, or social interaction, creating a sense of pleasure and satisfaction. This reinforcement reinforces behaviors, leading us to repeat them in the future.
Role of Dopamine in Motivation and Reward
- Dopamine and the Reward Pathway: When we engage in rewarding activities, the neural pathway known as the reward pathway becomes activated. Dopamine-releasing neurons in the VTA send signals to the nucleus accumbens, a brain region associated with reward, motivation, and pleasure. This surge of dopamine creates a positive reinforcement, encouraging us to engage in those activities more frequently.
Table 1: Role of Dopamine in Motivation and Reward
| Reward Stimulus | Dopamine Release | Behavioral Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Food | Increased | Increased food intake |
| Money | Increased | Increased monetary pursuits |
| Social Interaction | Increased | Increased social engagement |
| Drug Use | Increased | Drug addiction and dependence |
Role of Dopamine in Learning and Memory
-
Dopamine and Classical Conditioning: Dopamine is also involved in classical conditioning, where an initially neutral stimulus becomes associated with a rewarding stimulus. When the neutral stimulus is presented before the reward, dopamine is released, creating a conditioned response.
-
Dopamine and Working Memory: Dopamine plays a crucial role in working memory, the temporary storage of information in the brain. It enhances the ability to retain and manipulate information, improving cognitive function.
Role of Dopamine in Attention and Focus
-
Dopamine and Attention: Dopamine is essential for directing attention and focus. It facilitates the selection of relevant information from the environment, allowing us to concentrate on specific tasks.
-
Dopamine and Executive Function: Dopamine is involved in executive function, the higher-order cognitive processes such as planning, decision-making, and impulse control. It helps initiate and inhibit behaviors, enabling us to respond appropriately to different situations.
Table 2: Role of Dopamine in Learning and Memory
| Cognitive Process | Dopamine Release | Behavioral Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Classical Conditioning | Increased | Association of neutral and rewarding stimuli |
| Working Memory | Increased | Enhanced information retention and manipulation |
Pathologies Associated with Dopamine
Dysregulation of dopamine signaling is implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders:
-
Parkinson’s Disease: Dopamine depletion in the substantia nigra causes impaired motor control, tremors, and rigidity.
-
Schizophrenia: Hyperactivity in dopamine circuits in the brain is associated with hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking.
-
Addiction: Dopamine’s reinforcing effects contribute to the development of addiction to drugs, alcohol, and other substances.
Applications of Dopamine Research
Understanding dopamine’s functions has led to groundbreaking applications in various fields:
-
Pharmacology: Dopamine agonists and antagonists are used to treat neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia.
-
Neuroscience: Research on dopamine provides insights into brain function, learning, and motivation.
-
Mental Health: Dopamine dysregulation is a target for developing treatments for mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Table 3: Pathologies Associated with Dopamine
| Disorder | Dopamine Dysfunction | Behavioral Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Parkinson’s Disease | Dopamine depletion | Tremors, rigidity, impaired motor control |
| Schizophrenia | Dopamine hyperactivity | Hallucinations, delusions, disordered thinking |
| Addiction | Dopamine reinforcement | Substance dependence, impaired decision-making |
Pain Points and Motivations Related to Dopamine
Pain Points:
- Dopamine dysregulation can lead to severe neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Understanding dopamine’s functions is crucial for developing effective treatments.
Motivations:
- Researchers strive to elucidate dopamine’s role in cognitive processes and pathological conditions.
- Pharmaceutical companies seek to develop drugs that target dopamine signaling for therapeutic purposes.
Tips and Tricks for Maximizing Dopamine Function
-
Engage in Rewarding Activities: Participate in activities that bring you pleasure and satisfaction to stimulate dopamine release.
-
Practice Mindfulness and Gratitude: Pay attention to the positive aspects of your life to enhance dopamine’s reinforcing effects.
-
Get Adequate Sleep: Sleep deprivation can deplete dopamine levels, impairing cognitive function.
-
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes dopamine release, boosting motivation and mood.
Why Dopamine Matters
Dopamine is a vital neurotransmitter that significantly influences our behavior, learning, and mental well-being. Its dysregulation underlies various neurological and psychiatric disorders, highlighting the importance of understanding its functions. Research on dopamine continues to pave the way for advancements in pharmacology, neuroscience, and the treatment of mental health conditions.
Table 4: Tips and Tricks for Maximizing Dopamine Function
| Tip | Mechanism | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Engage in Rewarding Activities | Dopamine release | Enhanced motivation, pleasure, and satisfaction |
| Practice Mindfulness and Gratitude | Positive reinforcement | Increased dopamine sensitivity and resilience |
| Get Adequate Sleep | Dopamine replenishment | Improved cognitive function and mood |
| Exercise Regularly | Dopamine production | Boosted motivation, mood, and physical well-being |
Benefits of Understanding Dopamine
- Enhanced understanding of brain function and behavior.
- Improved diagnosis and treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Development of novel therapeutic interventions.
- Promotion of mental health and well-being.
Conclusion
Dopamine is a pivotal neurotransmitter in AP Psychology that plays a fundamental role in motivation, reward, learning, attention, and focus. Its dysregulation underlies various neurological and psychiatric disorders, demonstrating the significance of understanding its functions for developing effective treatments. Research on dopamine continues to provide groundbreaking insights into brain function and the development of novel applications in pharmacology, neuroscience, and mental health care.