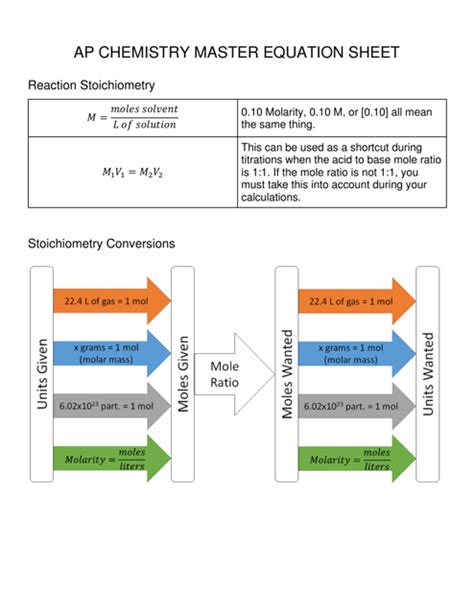
Navigating the complex world of chemistry requires a solid understanding of the chemical equations that govern countless reactions. Whether you’re a student grappling with stoichiometry or a professional seeking to unravel the intricacies of chemical processes, a comprehensive chemistry equations sheet serves as an invaluable resource. This comprehensive article provides a comprehensive guide to the chemistry equations sheet, empowering you with the knowledge and tools to conquer any chemical equation you encounter.

Purpose and Significance of a Chemistry Equations Sheet
At its core, a chemistry equations sheet is an indispensable tool that assists individuals in deciphering, balancing, and manipulating chemical equations. By providing a compilation of frequently used equations, formulas, and conversion factors, it alleviates the need for memorizing a multitude of individual equations, streamlining the process of solving chemical problems.
For students, a chemistry equations sheet serves as a valuable reference guide, ensuring they have essential information at their fingertips during exams and assignments. It can significantly enhance problem-solving efficiency, reducing the time spent searching for equations and freeing up cognitive resources for critical thinking.
In the workplace, professionals rely on chemistry equations sheets to optimize processes, design experiments, and interpret experimental data accurately. They provide a quick and reliable reference for complex reactions, ensuring that calculations are performed correctly and minimizing errors.
Components of a Chemistry Equations Sheet
The contents of a chemistry equations sheet vary depending on the intended audience and level of detail required. However, some common components include:
- Balanced Chemical Equations: A comprehensive list of balanced chemical equations for common reactions, including combustion, acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and gas evolution reactions.
- Conversion Factors: Unit conversion factors for converting between different units of measurement, such as grams to moles, liters to milliliters, and Celsius to Kelvin.
- Thermochemical Data: Information on the enthalpy changes associated with chemical reactions, including standard enthalpies of formation, bond energies, and heat capacities.
- Gas Laws and Equilibrium Constants: Equations and constants related to gas behavior and chemical equilibrium, such as the ideal gas law, the equilibrium constant expression, and the Le Chatelier’s principle.
- Electrochemical Data: Equations and constants related to electrochemistry, such as the Nernst equation, the standard reduction potentials, and the Faraday constant.
Effective Use of a Chemistry Equations Sheet
To maximize the benefits of using a chemistry equations sheet, follow these strategies:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Content: Take time to review the equations and data on the sheet and identify the most commonly used equations for your specific field of interest.
- Practice Regularly: Solve practice problems using the equations sheet to reinforce your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills.
- Supplement with Textbooks and Notes: While the equations sheet provides a valuable overview, it’s essential to supplement it with information from textbooks, lecture notes, and other sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of chemical concepts.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Be mindful of these pitfalls when using a chemistry equations sheet:
- Incorrectly Balanced Equations: Ensure that the equations you use are balanced to accurately represent the stoichiometry of the reaction.
- Unit Conversion Errors: Pay attention to unit conversions and ensure that you’re using the correct conversion factors to avoid incorrect results.
- Misapplication of Equations: Choose the appropriate equation for the specific reaction you’re studying and avoid applying equations outside of their intended scope.
Innovative Applications of Chemistry Equations
The versatility of chemistry equations extends beyond their traditional uses. By leveraging equations and data in innovative ways, scientists and engineers are unlocking new possibilities:
- Predicting Reaction Outcomes: Using computational models and large databases of chemical equations, researchers can predict the products and yields of complex reactions, optimizing processes and reducing experimental time.
- Designing New Materials: By understanding the chemical equations involved in material synthesis, scientists can tailor materials with specific properties, revolutionizing fields such as electronics, energy storage, and biomedicine.
- Developing Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Chemistry equations form the basis of diagnostic techniques such as spectrophotometry and chromatography, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of diseases.
Conclusion
A comprehensive chemistry equations sheet serves as a powerful tool for students and professionals alike, providing a wealth of information at their fingertips. By effectively utilizing the equations and data on the sheet, individuals can streamline problem-solving, enhance their understanding of chemical concepts, and unlock innovative applications in various fields.
Tables
Table 1: Common Combustion Reactions
| Reactants | Products | ΔH° (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O | -891 | |
| C₂H₅OH + 3O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O | -1367 | |
| NH₃ + 2O₂ → HNO₃ + H₂O | -365 |
Table 2: Unit Conversion Factors
| Quantity | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Length | 1 cm = 10⁻² m |
| Mass | 1 g = 10⁻³ kg |
| Volume | 1 L = 10⁻³ m³ |
| Temperature | 1 K = 273.15°C |
Table 3: Thermochemical Data
| Substance | ΔH°f (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| H₂O (l) | -286 |
| CO₂ (g) | -394 |
| CH₄ (g) | -75 |
Table 4: Gas Laws and Equilibrium Constants
| Equation | Constant |
|---|---|
| Ideal Gas Law | PV = nRT |
| Equilibrium Constant Expression | Kc = [C]c[D]d / [A]a[B]b |
| Le Chatelier’s Principle | An increase in the concentration of reactants will shift the equilibrium towards the products. |