Introduction

Higher education is often seen as the path to a successful career, but there are two primary pathways to obtaining that higher education: community college and university. While both offer different opportunities, the question of which one is right for you depends on your individual goals, interests, and financial situation. This comprehensive guide compares career options in community college versus university, providing you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision about your future.
Types of Career Options
Both community colleges and universities offer a wide range of career options, catering to various industries and sectors. Common career fields include:
Community College
* Healthcare: Nursing, Medical Assistant, Dental Hygienist
* Business: Accounting, Marketing, Management
* Technology: Computer Science, Information Systems, Cybersecurity
* Trade and Vocational: Automotive Technician, Electrician, Plumber
University
* Medicine: Doctor, Nurse Practitioner, Pharmacist
* Law: Lawyer, Judge, Legal Assistant
* Engineering: Civil Engineer, Mechanical Engineer, Chemical Engineer
* Business: Finance, Economics, Marketing
* Education: Teacher, Principal, Counselor
Career Pathways
Community College:
- Associate’s Degree: A two-year degree that provides foundational knowledge and skills in a specific field, preparing you for entry-level positions.
- Certificate Programs: Short-term programs that focus on developing specific skills or credentials, often in high-demand industries.
- Transfer Pathway: Many community colleges have agreements with universities, allowing you to transfer credits and pursue a bachelor’s degree.
University:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A four-year degree that provides comprehensive knowledge and research-based skills, qualifying you for professional or specialized roles.
- Master’s Degree: A one- to two-year graduate degree that expands your knowledge and expertise in a particular field, often leading to advanced career opportunities.
- Doctorate Degree: The highest level of academic achievement, typically required for research, teaching, or senior-level positions.
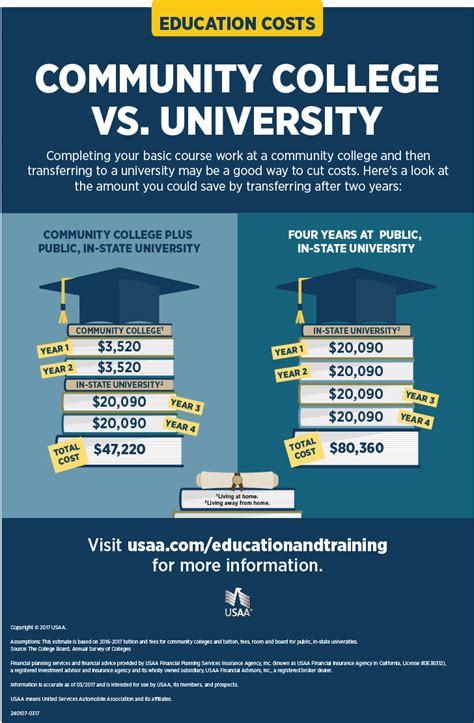
Cost and Time
The cost and time commitment of community college and university vary significantly.
Cost:
- Community College: Generally lower tuition and fees than universities.
- University: Higher tuition and fees, especially for private institutions.
Time:
- Associate’s Degree: Two years to complete.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Four years to complete.
- Master’s Degree: One to two years to complete.
- Doctorate Degree: Varies depending on the field and institution.
Pros and Cons
Community College
Pros:
- Lower cost and shorter time commitment
- Career-oriented programs
- Local and flexible options
- Provides a pathway to university transfer
Cons:
- May not offer all career options
- Limited research opportunities
- May not have the same prestige as a university degree
University
Pros:
- More career options and advanced degrees
- Comprehensive academic experience
- Research opportunities and faculty mentorship
- Higher earning potential
Cons:
- Higher cost and longer time commitment
- More competitive admissions process
- May not be as focused on career preparation
Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between community college and university depends on your individual circumstances and goals.
- Consider your career interests: If you are looking for specific job skills or certification, a community college may be a better option. However, if you are interested in pursuing an advanced degree or specialized career, a university may be more suitable.
- Evaluate your financial situation: Community college is generally more affordable, making it a good choice for students with financial constraints.
- Assess your academic preparedness: If you are not sure if you are ready for university-level coursework, a community college can provide a supportive learning environment to prepare you for transfer.
Innovative Applications
- Develop Dual-Enrollment Programs: Collaborate between community colleges and high schools to offer college-level courses to high school students, allowing them to earn college credits while still in high school.
- Create Industry-Driven Certificates: Partner with local businesses to develop certificate programs that align with specific industry needs, providing students with in-demand skills.
- Offer “Stackable” Credentials: Design programs that allow students to earn multiple credentials, such as associate’s degrees and certificates, that can be “stacked” to build upon each other and enhance their career prospects.
Tables for Comparative Analysis
Table 1: Common Career Options
| Career Field | Community College | University |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Nursing, Medical Assistant, Dental Hygienist | Doctor, Nurse Practitioner, Pharmacist |
| Business | Accounting, Marketing, Management | Finance, Economics, Marketing |
| Technology | Computer Science, Information Systems, Cybersecurity | Civil Engineer, Mechanical Engineer, Chemical Engineer |
| Trade and Vocational | Automotive Technician, Electrician, Plumber | Not Typically Offered |
Table 2: Career Pathways
| Pathway | Community College | University |
|---|---|---|
| Associate’s Degree | Entry-level positions | Transfer to university |
| Certificate Programs | Specific skills or credentials | Not typically offered |
| Transfer Pathway | Credits transfer to university | Not applicable |
Table 3: Cost and Time
| Metric | Community College | University |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition and Fees* | Generally lower | Higher |
| Time Commitment | Associate’s Degree: 2 years | Bachelor’s Degree: 4 years |
Table 4: Pros and Cons
| Community College | University |
|---|---|
| Pros: Lower cost, shorter time commitment, career-oriented programs | Pros: More career options, comprehensive academic experience, research opportunities, higher earning potential |
| Cons: Limited career options, no research opportunities, lower prestige | Cons: Higher cost, longer time commitment, competitive admissions, less focus on career preparation |
Conclusion
The decision between community college and university is a personal one. By carefully considering your career interests, financial situation, and academic preparedness, you can choose the path that will best prepare you for success in your chosen field. Both community colleges and universities offer valuable opportunities for career advancement. It is important to research the options available and make an informed decision that aligns with your individual goals and aspirations.