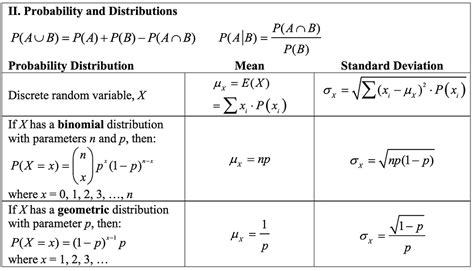
Welcome to AP Statistics Unit 5, where we dive into the realm of probability distributions, the fundamental building blocks of statistical inference. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intricacies of these mathematical models and their diverse applications across a wide array of fields.

Key Concepts and Definitions
Probability Distribution: A mathematical function that describes the probability of observing different values of a random variable.
Random Variable: A variable whose value is determined by chance.
Discrete Probability Distribution: A probability distribution for a random variable that can only take on a finite or countable number of values.
Continuous Probability Distribution: A probability distribution for a random variable that can take on any value within a specified range.
Types of Probability Distributions
Discrete Probability Distributions
- Binomial Distribution: Models the number of successes in a sequence of independent trials.
- Poisson Distribution: Models the number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space.
- Hypergeometric Distribution: Models the number of successes in drawing without replacement from a finite population.
Continuous Probability Distributions
- Normal Distribution: A bell-shaped distribution that is ubiquitous in nature and statistics.
- Uniform Distribution: A distribution where all values within a specified range are equally likely.
- Exponential Distribution: A distribution that models the time until a random event occurs.
- Gamma Distribution: A distribution that extends the exponential distribution and is used in a variety of applications.
Applications of Probability Distributions
Probability distributions have far-reaching applications in various domains, including:
- Business and Finance: Predicting consumer spending, modeling financial risk, and optimizing inventory management.
- Healthcare: Assessing disease prevalence, evaluating treatment efficacy, and predicting patient outcomes.
- Engineering: Designing reliable systems, predicting equipment failures, and optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Social Science: Understanding population behavior, modeling survey responses, and analyzing voting patterns.
- Quality Control: Monitoring production processes, detecting defects, and ensuring product safety.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with probability distributions, it is essential to avoid common pitfalls:
- Misidentifying the Type of Distribution: Incorrectly assuming a distribution is discrete when it is continuous or vice versa.
- Misinterpreting Probabilities: Confusing the probability of one event occurring with the probability of another.
- Using the Wrong Parameters: Selecting inappropriate parameters for a given probability distribution.
- Ignoring Context: Failing to consider the underlying assumptions and limitations of a probability distribution.
Step-by-Step Approach to Using Probability Distributions
- Identify the Random Variable: Determine the characteristic being measured and considered random.
- Classify the Distribution: Determine whether the distribution is discrete or continuous.
- Calculate Parameters: Find the parameters (e.g., mean, standard deviation) that characterize the distribution.
- Draw the Distribution: Plot the probability density function or probability mass function to visualize the distribution.
- Calculate Probabilities: Use the probability distribution to calculate the probability of specific events.
- Make Inferences: Draw conclusions about the random variable based on the probability distribution.
Innovative Applications of Probability Distributions
Beyond traditional applications, probability distributions can fuel innovative solutions:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Training AI models to learn from data, predict outcomes, and optimize decision-making.
- Precision Medicine: Developing personalized treatments and therapies tailored to individual patients.
- Cybersecurity: Detecting anomalous behavior, identifying threats, and protecting critical infrastructure.
- Behavioral Economics: Understanding and predicting human decision-making in the face of uncertainty.
Conclusion
AP Statistics Unit 5 on probability distributions equips students with a powerful set of tools that empower them to analyze, interpret, and understand randomness in the world around them. From modeling consumer behavior to predicting natural disasters, probability distributions play an integral role in shaping our future and driving innovation.
Additional Resources
- The Art of Statistics
- Khan Academy Probability Distributions
- MIT OpenCourseWare Probability and Statistics
Tables
Table 1: Types of Probability Distributions
| Type | Discrete/Continuous | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Binomial | Discrete | Number of successes in trials |
| Poisson | Discrete | Number of events in a fixed interval |
| Normal | Continuous | Height of adults, IQ scores |
| Exponential | Continuous | Time until a failure occurs |
| Gamma | Continuous | Waiting time until a specific event |
Table 2: Applications of Probability Distributions
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Business | Predicting demand, modeling risk |
| Healthcare | Assessing disease risk, evaluating treatments |
| Engineering | Designing reliable systems, predicting equipment failures |
| Social Science | Understanding voting patterns, analyzing survey responses |
| Quality Control | Monitoring production, detecting defects |
Table 3: Common Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Misidentifying Distribution | Assuming a distribution is discrete when it is continuous |
| Misinterpreting Probabilities | confusing the probability of one event with another |
| Using the Wrong Parameters | Selecting inappropriate parameters for a distribution |
| Ignoring Context | Failing to consider the assumptions and limitations of a distribution |
Table 4: Innovative Applications of Probability Distributions
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| AI | Training models, predicting outcomes |
| Precision Medicine | Developing personalized treatments |
| Cybersecurity | Detecting threats, protecting infrastructure |
| Behavioral Economics | Understanding human decision-making |