Standard deviation, a fundamental concept in statistics, plays a crucial role in AP Psychology. It quantifies the variability or spread of data, providing insights into the distribution and consistency of psychological phenomena. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of standard deviation, exploring its significance, applications, and interpretation within the AP Psychology curriculum.

Understanding Standard Deviation
Standard deviation, denoted by the Greek letter σ (sigma), measures how far individual data points deviate from the mean (average) of a distribution. It represents the average distance from the mean, thereby indicating the extent to which data is dispersed or clustered. A higher standard deviation implies greater variability, while a lower standard deviation indicates less variability.
Calculating Standard Deviation
Calculating standard deviation involves the following steps:
- Determine the mean: Add up all the data points and divide by the total number of points.
- Calculate the variance: For each data point, subtract the mean, square the result, and add these squared differences together. Then, divide the sum by the total number of points minus one (degrees of freedom).
- Take the square root: The square root of the variance is the standard deviation.
Significance of Standard Deviation in AP Psychology
Standard deviation holds immense importance in AP Psychology as it allows researchers and psychologists to:
- Describe data distributions: It provides a concise summary of the spread of data, enabling researchers to characterize the variability within a sample.
- Make inferences: Standard deviation facilitates the estimation of population parameters from sample data. By understanding the distribution of a sample, psychologists can make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn.
- Conduct hypothesis testing: Standard deviation is essential for hypothesis testing, as it allows researchers to determine whether observed differences between groups are statistically significant or due to chance.
Applications of Standard Deviation in AP Psychology
Standard deviation finds widespread applications in psychological research and practice:
- Personality assessment: Standard deviation is used to determine the variability of personality traits within a population.
- Intelligence testing: Standard deviation helps establish norms for intelligence tests, enabling psychologists to compare an individual’s score against the population average.
- Clinical diagnosis: Standard deviation assists in distinguishing between normal and abnormal psychological functioning. For instance, it can help identify individuals with unusually high or low levels of anxiety or depression.
Interpreting Standard Deviation
Interpreting standard deviation requires consideration of the following guidelines:
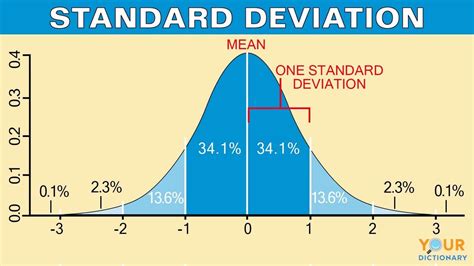
- Rule of thumb: Approximately 68% of data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations.
- Contextual factors: The interpretation of standard deviation should consider the specific research question and the context in which it is applied.
- Comparison to norms: Comparing standard deviations across different samples or populations can provide insights into relative variability and consistency.
Tables for Standard Deviation
| Range of z-scores | Percentage of data |
|---|---|
| Within 1 standard deviation of the mean | 68% |
| Within 2 standard deviations of the mean | 95% |
| Within 3 standard deviations of the mean | 99.7% |
| z-score | Probability |
|---|---|
| -2.58 | 0.01 |
| -2.33 | 0.02 |
| -1.96 | 0.05 |
| -1.645 | 0.10 |
| -1.282 | 0.20 |
| -1.036 | 0.30 |
| -0.674 | 0.50 |
| 0.674 | 0.50 |
| 1.036 | 0.30 |
| 1.282 | 0.20 |
| 1.645 | 0.10 |
| 1.96 | 0.05 |
| 2.33 | 0.02 |
| 2.576 | 0.01 |
Effective Strategies for Using Standard Deviation
- Use a calculator or statistical software: Calculating standard deviation by hand can be tedious. Utilize appropriate tools to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Consider the sample size: Smaller sample sizes tend to produce larger standard deviations due to sampling variability.
- Outliers: Identify and handle outliers (extreme data points) carefully, as they can significantly affect the standard deviation.
- Interpret standard deviation in context: Understand the specific research question and the context in which standard deviation is applied to draw meaningful conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between standard deviation and variance? Variance is the square of standard deviation. Standard deviation is expressed in the same units as the original data, making it easier to interpret.
- Can standard deviation be negative? No, standard deviation is always positive or zero.
- How do I use standard deviation to compare groups? By comparing the standard deviations of different groups, researchers can gain insights into the relative variability and consistency of the groups.
- What is the standard deviation of a normal distribution? The standard deviation of a normal distribution is 1.
- How is standard deviation used in hypothesis testing? Standard deviation helps determine the probability of obtaining a sample statistic as extreme as the one observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true. This information is crucial for making statistical decisions.
- How can standard deviation be used to improve research design? Understanding the standard deviation of a sample can guide researchers in determining the optimal sample size and data collection methods to achieve reliable and precise results.
Conclusion
Standard deviation is a critical concept in AP Psychology that provides a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing psychological data. By mastering the calculation, interpretation, and application of standard deviation, students can gain a deeper understanding of the variability and consistency of psychological phenomena, enhancing their ability to conduct research and draw informed conclusions.