The chemical structure of chlorine fluoride (CLF) holds immense significance in understanding its properties and potential applications. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the CLF Lewis structure, its molecular geometry, bonding, polarity, and applications.

Lewis Structure of Chlorine Fluoride
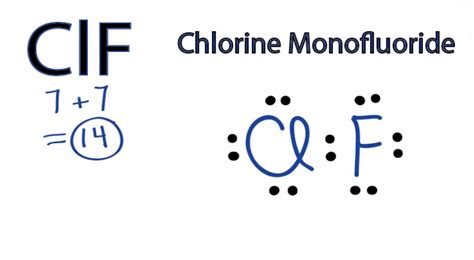
The Lewis structure of chlorine fluoride depicts the arrangement of valence electrons and atoms within the molecule. It is represented as:
Cl:F
In this structure, chlorine (Cl) has seven valence electrons, fluorine (F) has one, and the shared electron pair forms a single covalent bond between the two atoms.
Molecular Geometry and Bonding
The Lewis structure of CLF suggests a linear molecular geometry. The chlorine and fluorine atoms are arranged linearly, with the Cl-F bond length measuring approximately 1.63 Å. This linear arrangement is attributed to the sp hybridization of chlorine and the sp³ hybridization of fluorine.
The Cl-F bond is a polar covalent bond, meaning that the electron pair is not shared equally between the atoms. Chlorine, being more electronegative than fluorine, attracts the electron pair towards itself, resulting in a partial negative charge on fluorine and a partial positive charge on chlorine.
Polarity and Dipole Moment
The polarity of the Cl-F bond gives rise to a molecular dipole moment of 0.87 D. This dipole moment indicates that the molecule has a slight separation of positive and negative charges, making it polar.
Applications of Chlorine Fluoride
CLF finds applications in various fields, including:
- Etching: CLF is employed as an etchant for silicon and other semiconductors in the microelectronics industry.
- Rocket Propellant: CLF has been used as a high-energy oxidizer in rocket propellants.
- Chemical Warfare Agent: CLF was once considered as a potential chemical warfare agent, but its use has been prohibited under the Chemical Weapons Convention.
Key Properties of Chlorine Fluoride
The following table summarizes the key properties of CLF:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 54.46 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | -100.0 °C |
| Melting Point | -153.8 °C |
| Density | 1.74 g/cm³ at 0 °C |
| Molecular Dipole Moment | 0.87 D |
Market Analysis and Value Proposition
The global chlorine fluoride market is estimated to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.5%. The increasing demand for CLF in semiconductor etching applications is expected to drive market growth.
Innovations and Applications
Researchers are exploring new applications for CLF, including:
- Hydrogen Fluoride Production: CLF can be used to produce hydrogen fluoride (HF), a valuable industrial chemical.
- Battery Electrolytes: CLF is being investigated as a component in high-performance battery electrolytes.
Strategies for Success in the CLF Market
To succeed in the CLF market, manufacturers should focus on the following strategies:
- Develop high-purity CLF: Customers demand CLF with high purity for sensitive applications such as semiconductor etching.
- Innovation and R&D: Invest in research and development to explore new applications and improve production processes.
- Cost optimization: Optimize production processes to reduce costs and maintain competitiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the bond length of the Cl-F bond in CLF?
1.63 Å
2. Is CLF a polar molecule?
Yes, due to the polar nature of the Cl-F bond.
3. What are the main applications of CLF?
Etching, rocket propellants, and chemical warfare agents.
4. What is the estimated market size of CLF by 2028?
USD 1.2 billion
5. How can manufacturers improve their competitiveness in the CLF market?
Focus on high purity, innovation, and cost optimization.
6. What are potential new applications for CLF?
Hydrogen fluoride production and battery electrolytes.
Conclusion
The CLF Lewis structure provides insights into the molecular architecture and properties of chlorine fluoride. Its linear geometry, polar bond, and dipole moment contribute to its diverse applications, including etching, rocket propellants, and chemical warfare agents. As research continues, new applications are emerging, driving the growth of the global CLF market.