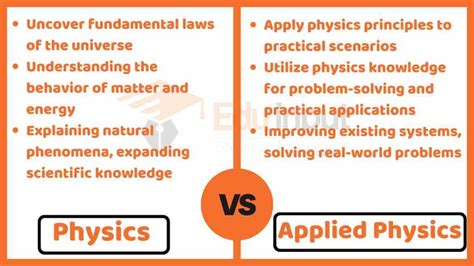
Physics, the fundamental study of matter, energy, and their interactions, serves as the bedrock of our understanding of the universe. Applied physics, on the other hand, takes the principles of physics and applies them to practical problems, leading to the development of innovative technologies that enhance our lives.

Understanding the Distinctions: Theoretical vs. Practical Focus
Physics explores the fundamental properties and behaviors of the physical world, aiming to unravel the laws governing the universe. It embraces theoretical concepts, mathematical models, and experimental investigations to deepen our knowledge of the cosmos.
Applied physics harnesses the principles of physics to solve real-world problems. It involves the design, development, and implementation of practical applications that cater to specific needs in various fields, including engineering, medicine, and industry.
Applied Physics: A Catalyst for Innovation
Applied physics plays a pivotal role in the advancement of modern technologies. Here are a few key examples:
- Medical Imaging: Applied physics empowers medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI to aid in disease diagnosis and treatment.
- Renewable Energy: Applied physics enables the development of solar panels and wind turbines to harness clean energy sources and mitigate climate change.
- Nanotechnology: Applied physics fuels advancements in nanotechnology, leading to the creation of novel materials and devices with exceptional properties.
Benefits of Applied Physics
The benefits of applied physics extend far beyond the laboratory walls:
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Applied physics applications improve healthcare, energy efficiency, and technological advancements, contributing to a better quality of life.
- Economic Growth: Applied physics-driven industries stimulate economic growth and create new job opportunities in engineering, manufacturing, and research.
- Environmental Sustainability: Applied physics solutions, such as renewable energy technologies, promote environmental sustainability and mitigate the impact of human activities.
Pros and Cons: A Balanced Assessment
While applied physics offers immense benefits, it also has certain limitations:
Pros:
- Practical Applications: Applied physics focuses on solving real-world problems, leading to tangible outcomes.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Applied physicists collaborate with engineers, scientists, and clinicians to bridge the gap between fundamental research and practical applications.
- Economic Impact: Applied physics-driven industries generate revenue and create jobs, contributing to economic growth.
Cons:
- Technological Challenges: Applied physics projects often face technical challenges that require innovative solutions.
- Time-Consuming Processes: Developing and implementing applied physics solutions can be time-consuming, requiring patience and perseverance.
- Resource-Intensive: Applied physics research and development require significant resources, including funding, infrastructure, and specialized expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What industries use applied physics?
– Applied physics finds application in fields such as healthcare, energy, manufacturing, transportation, electronics, and materials science. -
What are the career opportunities in applied physics?
– Applied physicists work in research institutions, industries, hospitals, and government agencies, pursuing roles in development, manufacturing, and quality control. -
How does applied physics differ from engineering?
– Engineering focuses on designing and building practical systems, while applied physics bridges the theoretical concepts of physics with practical applications. -
What are some emerging trends in applied physics?
– Quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and nanotechnology are among the rapidly advancing areas of applied physics research. -
How can we foster innovation in applied physics?
– Investment in research and education, interdisciplinary collaboration, and public awareness are crucial for fostering innovation in applied physics. -
What are the ethical implications of applied physics?
– Applied physicists should consider the ethical and societal impacts of their research and applications, ensuring responsible development and deployment.
Conclusion: A Synergistic Relationship
Applied physics stands as a transformative force, harnessing the power of physics to address real-world challenges. While distinct from pure physics in its focus on practical applications, applied physics complements fundamental research by providing a pathway for translating theoretical insights into tangible technologies that enhance our lives.
As we continue to unlock the mysteries of the universe, applied physics will remain an indispensable tool for shaping a future where scientific advancements empower human progress and societal well-being.