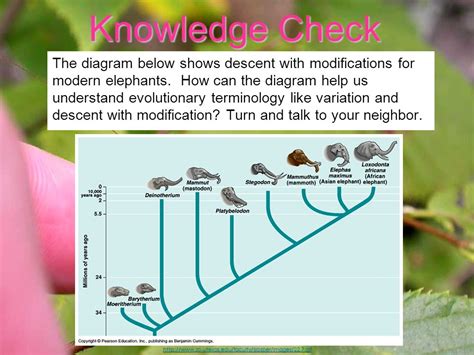
Introduction

Darwin’s theory of evolution, known as descent with modification, describes the gradual change of living organisms over many generations. This process involves the accumulation of genetic variation, which results in phenotypic changes that can enhance survival and reproductive success.
Mechanism of Descent with Modification
The primary mechanisms driving descent with modification are:
- Variation: Genetic variation within a population arises from mutations, gene flow, genetic drift, and sexual recombination.
- Natural Selection: Individuals with traits that increase their survival and reproduction rate in a given environment are more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation.
- Heredity: Traits that confer an advantage are inherited by offspring, allowing the advantageous adaptations to spread through the population.
Evidence for Descent with Modification
Overwhelming evidence supports the theory of descent with modification, including:
- Fossil Record: Fossils document the gradual changes in organisms over millions of years, showing a continuum from ancestral to modern species.
- Comparative Anatomy: Homologous structures in different species, such as the forelimbs of mammals, indicate common ancestry.
- Molecular Biology: DNA and protein sequences show genetic similarities between species, providing evidence of relatedness.
Descent with Modification in Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions on descent with modification often assess students’ understanding of the following concepts:
- The mechanisms of evolution: Variation, natural selection, and heredity
- The evidence for evolution: Fossil record, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology
- The evolutionary history of different species: Phylogenetic trees and cladistics
- The impact of evolution on biodiversity: Speciation, extinction, and ecosystem dynamics
Sample Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following is NOT a mechanism of evolution?
* (A) Variation
* (B) Mutation
* (C) Inheritance
* (D) Artificial selection -
The gradual change of organisms over many generations is known as:
* (A) Descent with modification
* (B) Speciation
* (C) Adaptation
* (D) Natural selection -
Which of the following provides evidence for common ancestry?
* (A) Homologous structures
* (B) Convergent evolution
* (C) Analogous structures
* (D) Vestigial structures
Answer Key
- D
- A
- A
Key Concepts for Multiple Choice Questions
- Variation: The raw material for natural selection
- Natural Selection: The driving force of evolution
- Heredity: The transmission of traits from one generation to the next
- Fossil Record: Direct evidence of evolutionary change
- Comparative Anatomy: Structural similarities indicative of common ancestry
Conclusion
Descent with modification is a fundamental concept in biology that explains the diversity of life on Earth. Multiple choice questions on this topic assess students’ understanding of the mechanisms, evidence, and implications of evolution. By mastering these concepts, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the process that has shaped the living world.