Introduction

Mitosis and meiosis are crucial processes involved in cell division. While both are essential for different types of cell reproduction, they differ in purpose and outcomes. This test will challenge your understanding of mitosis and meiosis, helping you assess your knowledge of their characteristics and significance.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which type of cell division results in two genetically identical daughter cells?
(a) Mitosis
(b) Meiosis
(c) Apoptosis
(d) Differentiation
2. The number of chromosomes in a daughter cell after mitosis is:
(a) Half the number in the parent cell
(b) The same as the number in the parent cell
(c) Double the number in the parent cell
(d) Variable, depending on the cell type
3. Which of the following is NOT a stage of mitosis?
(a) Prophase
(b) Metaphase
(c) Anaphase II
(d) Telophase
4. The crossing over of homologous chromosomes occurs during which stage of meiosis?
(a) Prophase I
(b) Metaphase II
(c) Anaphase I
(d) Telophase II
5. Which type of cell division is responsible for gamete formation?
(a) Mitosis
(b) Meiosis
(c) Transcription
(d) Translation
True/False Questions
1. Mitosis occurs only in somatic cells.
(True/False)
2. Meiosis results in four genetically identical daughter cells.
(True/False)
3. The spindle fibers are responsible for separating chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.
(True/False)
4. Interphase is a stage of both mitosis and meiosis.
(True/False)
5. Homologous chromosomes are identical copies of each other.
(True/False)
Answer Key
Multiple Choice
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
- (a)
- (b)
True/False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
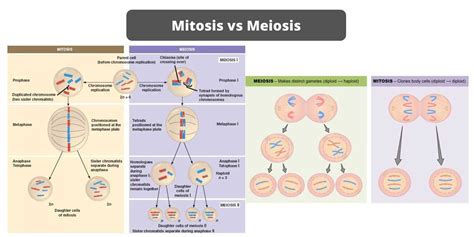
Detailed Comparisons: Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Purpose:
- Mitosis: Growth, repair, and cell replacement
- Meiosis: Gamete (sex cell) formation
Number of Daughter Cells:
- Mitosis: 2
- Meiosis: 4
Number of Divisions:
- Mitosis: 1
- Meiosis: 2
Chromosome Number:
- Mitosis: Daughter cells have diploid (2n) number of chromosomes
- Meiosis: Daughter cells have haploid (n) number of chromosomes
Chromosome Pairing:
- Mitosis: No homologous chromosome pairing
- Meiosis: Homologous chromosome pairing and recombination
Synapsis:
- Mitosis: No synapsis
- Meiosis: Homologous chromosomes physically connect and undergo synapsis
Crossing Over:
- Mitosis: No crossing over
- Meiosis: Crossing over occurs during prophase I, resulting in genetic recombination
Significance:
Mitosis:
- Essential for growth and repair in multicellular organisms
- Replacement of damaged or worn-out cells
- Production of daughter cells with identical genetic makeup to the parent cell
Meiosis:
- Sexual reproduction and gamete formation
- Halving of chromosome number for genetic diversity
- Removal of mutations and genetic redundancy
Applications
- Cancer Treatment: Targeting mitosis in cancer cells can inhibit tumor growth.
- Fertility Treatments: Understanding meiosis is crucial for assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF.
- Genetic Diseases: Studying meiosis can help diagnose and treat genetic disorders related to chromosome abnormalities.
Tips and Tricks for Scoring High
- Understand the fundamental concepts of cell division.
- Distinguish between the key differences between mitosis and meiosis.
- Practice using tables and diagrams to summarize information.
- Review authoritative sources such as textbooks and scientific journals.
- Consult with teachers or experts for clarification.
Conclusion
This test provided a comprehensive assessment of your knowledge of mitosis and meiosis. By understanding the characteristics and significance of these processes, you have gained a deeper appreciation of their role in life science and its various applications.