Discover the Essence of Area and Perimeter: A Comprehensive Guide
Geometry can often evoke a sense of trepidation, but with the right tools and a clear understanding, you can navigate its complexities with ease. One indispensable tool is the area and perimeter anchor chart, a priceless resource that serves as your compass in the fascinating realm of shapes.

Area and Perimeter: Unlocking the Concepts
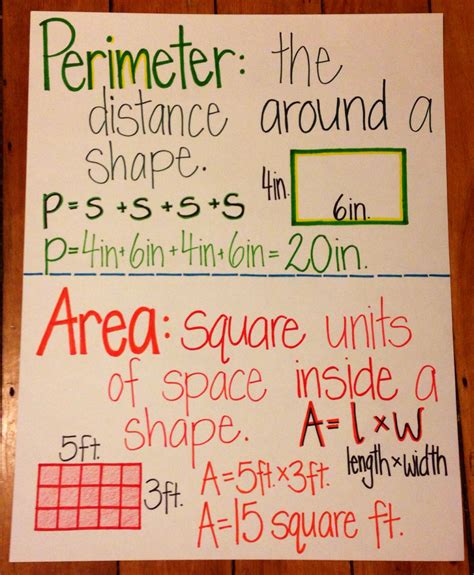
Area represents the measure of the surface enclosed within a shape’s boundaries. It quantifies the size of the two-dimensional space occupied by the shape. Measured in square units (such as square centimeters or square meters), area provides an essential understanding of a shape’s size and capacity.
Perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary surrounding a shape. It encapsulates the distance around the outside edge of the shape. Measured in linear units (such as centimeters or meters), perimeter plays a crucial role in determining the shape’s length, height, and overall dimensions.
Anchor Chart: Your Guiding Light
An area and perimeter anchor chart is a visual representation that empowers you to calculate area and perimeter with accuracy. It provides a concise summary of formulas and definitions, ensuring you have the building blocks to solve geometrical problems with confidence.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Applications
The applications of area and perimeter extend far beyond the classroom. These concepts find practical use in myriad fields, including:
- Architecture: Architects rely on area and perimeter calculations to design buildings, optimize space utilization, and ensure structural integrity.
- Engineering: Engineers use these principles to analyze the strength of materials, design bridges and roads, and create efficient machinery.
- Landscaping: Landscape architects leverage area and perimeter to plan outdoor spaces, calculate the coverage of lawns and gardens, and design irrigation systems.
- Construction: Builders utilize area and perimeter measurements to determine the amount of materials needed, calculate labor costs, and estimate project timelines.
- Interior Design: Interior designers rely on these concepts to optimize space, create functional layouts, and enhance the aesthetics of interiors.
Tables for Enhanced Understanding
To further solidify your understanding, we present four comprehensive tables that showcase the formulas and applications of area and perimeter:
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Square | A = s² | P = 4s |
| Rectangle | A = lw | P = 2(l + w) |
| Triangle | A = ½bh | P = a + b + c |
| Circle | A = πr² | P = 2πr |
| Application | Area | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Painting a Wall | Calculate the area to estimate paint quantity | Measure the perimeter to determine the amount of trim needed |
| Fencing a Yard | Determine the area to calculate the amount of grass seed | Measure the perimeter to purchase the required fencing |
| Designing a Garden | Plan the area for planting and landscaping | Calculate the perimeter for the edging or borders |
| Remodeling a Kitchen | Measure the area for flooring and cabinets | Determine the perimeter for baseboards and counter space |
Engaging with Customers: Asking the Right Questions
To fully comprehend your customers’ viewpoints and address their needs effectively, ask these probing questions:
- What are the specific area and perimeter requirements of your project?
- How will area and perimeter calculations impact the design and implementation of your solution?
- What challenges have you faced in calculating area and perimeter in the past?
- How can we leverage area and perimeter measurements to optimize your project’s outcomes?
Effective Strategies for Customer Success
- Personalize the Experience: Tailor your approach to each customer’s unique needs and project specifications.
- Provide Clear Explanations: Use simple language and visual aids to illustrate area and perimeter concepts.
- Offer Practical Examples: Showcase real-world applications to demonstrate the relevance and value of these calculations.
- Encourage Collaboration: Invite customers to participate in the measurement process and provide feedback at every stage.
- Use Technology to Enhance Accuracy: Utilize digital tools and calculators to ensure precise measurements and calculations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How do I calculate the area of a complex shape?
A: Complex shapes can be divided into simpler shapes, and then the areas of those simpler shapes can be added together.
Q: Why is perimeter important in real-world applications?
A: Perimeter helps determine the length of fencing needed to enclose an area, the amount of trim required to finish a room, and the distance around a track or field.
Q: How can I improve my understanding of area and perimeter?
A: Practice solving problems, use visual aids like anchor charts, and engage in hands-on activities that involve measuring and calculating area and perimeter.
Q: What are some creative applications of area and perimeter?
A: Optimizing packing efficiency, designing ergonomic workspaces, and creating artistic patterns based on geometric shapes.