The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin) offers an exceptional Biology degree program that equips students with a comprehensive understanding of life sciences, preparing them for diverse career paths in academia, industry, and healthcare.

Program Overview
The UT Austin Biology degree is tailored to provide students with:
- A deep foundation in biological principles, including genetics, cell biology, biochemistry, and ecology
- Hands-on laboratory experience to hone practical skills in microscopy, molecular techniques, and data analysis
- Opportunities to specialize in specific areas of biology, such as molecular biology, ecology, evolution, and neuroscience
Curriculum and Requirements
The Bachelor of Science in Biology (B.S.) degree at UT Austin typically requires completing 120 semester credit hours, including:
- Core Biology Courses (33-38 hours): Fundamentals of Biology, Cell Biology, Genetics, Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Microbiology
- Laboratory Courses (12-14 hours): Accompanying labs for core courses
- Chemistry and Math Courses (16-18 hours): General Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Statistics
- Electives (37-52 hours): Courses in areas of interest, including specialty areas in biology, other sciences, or liberal arts
Specializations and Options
UT Austin’s Biology program offers various specializations that students can pursue to tailor their studies to their career aspirations:
- Biomedical Sciences: Prepares students for careers in medicine, dentistry, or other health professions
- Molecular Biology: Focuses on the structure, function, and regulation of genetic material
- Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior: Explores the interactions between organisms and their environment
- Neuroscience: Investigates the structure and function of the nervous system
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology: Integrates computational tools and techniques with biological data analysis
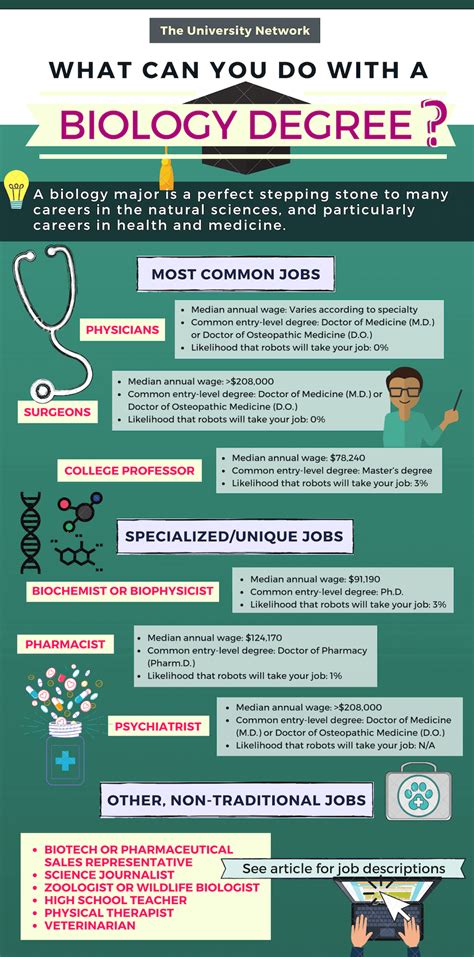
Career Paths for Biology Graduates
Graduates with a Bachelor of Science in Biology from UT Austin are well-prepared for careers in:
- Research: Conduct scientific studies in academia, government, or industry
- Education: Teach biology at secondary or post-secondary institutions
- Healthcare: Pursue careers as doctors, dentists, nurses, or healthcare researchers
- Environmental Science: Work in fields related to conservation, environmental management, or policy
- Industry: Engage in product development, quality control, or sales in biotechnology, pharmaceutical, or food companies
Figures and Statistics
- According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for biologists was $84,410 in May 2021.
- The American Institute of Biological Sciences (AIBS) reports that nearly 30% of biology bachelor’s degree holders pursue graduate studies within five years of graduation.
- The National Science Foundation (NSF) estimates that the demand for workers with bachelor’s degrees in biology will grow by 11% from 2019 to 2029.
Creative Applications of Biology
Beyond traditional career paths, biology graduates can also pursue innovative applications in emerging fields:
- Synthetic Biology: Design and engineer biological systems with novel functions
- Biomaterials: Develop materials with biological properties for use in medical implants, drug delivery, and tissue engineering
- Astrobiology: Explore the potential for life beyond Earth and its implications
- Agri-Technology: Apply biological principles to enhance agricultural practices and ensure food security
Useful Tables
Table 1: Core Biology Courses
| Course | Hours |
|---|---|
| Fundamentals of Biology | 4 |
| Cell Biology | 3 |
| Genetics | 3 |
| Evolutionary Biology | 3 |
| Ecology | 3 |
| Microbiology | 3 |
Table 2: Specializations and Focus Areas
| Specialization | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Biomedical Sciences | Molecular Mechanisms of Disease, Physiology |
| Molecular Biology | Genomics, Proteomics, Transcriptomics |
| Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior | Animal Behavior, Plant Ecology, Microbial Ecology |
| Neuroscience | Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology, Neuropharmacology |
| Bioinformatics and Computational Biology | Sequence Analysis, Bioinformatics Tools, Data Visualization |
Table 3: Career Paths for Biology Graduates
| Career Path | Median Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Bioscientist | $97,890 |
| Medical Scientist | $93,140 |
| Environmental Scientist | $73,450 |
| Science Teacher | $60,190 |
| Data Analyst | $91,410 |
Table 4: Biology Degree Statistics
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Median Starting Salary | $50,000-$60,000 |
| Employment Growth (2019-2029) | 11% |
| Graduate School Enrollment within 5 Years | 30% |
Conclusion
The UT Austin Biology degree program empowers students to explore the intricate world of life sciences, equipping them with a comprehensive foundation and specialized knowledge in their chosen field. Graduates are highly sought after in academia, industry, and healthcare, with diverse career paths that offer both intellectual fulfillment and impact on the world.