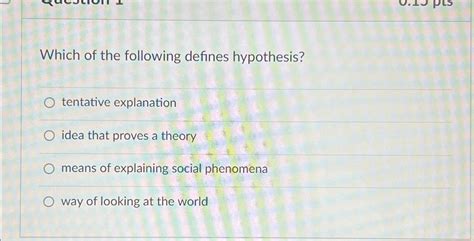
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon that has been tested or is being tested. It is a tentative statement that can be supported or refuted by evidence.

Here are the key elements of a hypothesis:
- It is testable. A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation.
- It is specific. A hypothesis must make a specific prediction about what will happen if the hypothesis is true.
- It is falsifiable. A hypothesis must be able to be proven false. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a valid hypothesis.
Here are some examples of hypotheses:
- Hypothesis: The rate of photosynthesis is proportional to the amount of light available.
- Hypothesis: The boiling point of a liquid is proportional to its molecular weight.
- Hypothesis: The number of stars in the universe is infinite.
The following does not define a hypothesis:
- A fact: A fact is a statement that is known to be true. For example, “The Earth is round.” is a fact.
- A theory: A theory is a well-supported explanation for a phenomenon that has been tested and confirmed by a large body of evidence. For example, “The theory of evolution” is a theory.
- A guess: A guess is a statement that is not based on evidence. For example, “I guess it will rain tomorrow.” is a guess.
Why Hypotheses Matter
Hypotheses are important because they allow us to make predictions about the world around us. They also help us to design experiments that can test our predictions. By testing our hypotheses, we can learn more about the world around us and how it works.
Benefits of Using Hypotheses
There are many benefits to using hypotheses in your research. Some of the benefits include:
- Hypotheses help you to focus your research. When you have a hypothesis, you know what you are trying to prove. This can help you to stay focused on your research and avoid getting sidetracked.
- Hypotheses help you to design better experiments. A well-designed experiment can help you to collect the data you need to test your hypothesis.
- Hypotheses help you to communicate your research. When you have a hypothesis, it is easier to explain your research to others.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are a few common mistakes that people make when using hypotheses. Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Making a hypothesis that is not testable. A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. If a hypothesis cannot be tested, then it is not a valid hypothesis.
- Making a hypothesis that is too broad. A hypothesis should be specific enough to make a prediction about what will happen if the hypothesis is true. If a hypothesis is too broad, then it will be difficult to test.
- Making a hypothesis that is not falsifiable. A hypothesis must be able to be proven false. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a valid hypothesis.
Conclusion
Hypotheses are an important part of the scientific process. They allow us to make predictions about the world around us and to design experiments that can test our predictions. By testing our hypotheses, we can learn more about the world around us and how it works.