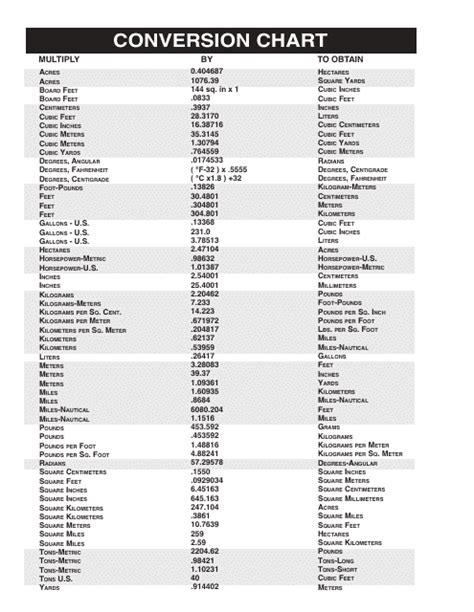
Introduction

Physics, the fundamental science that explores the nature and properties of matter and energy, relies heavily on precise measurements and calculations. As researchers delve into complex scientific investigations, they encounter a vast array of units and conversion factors that can present challenges in understanding and interpreting data. To overcome these hurdles, a comprehensive conversion chart for physics is an invaluable tool.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the most commonly used units in physics, along with their SI (International System of Units) equivalents and conversion factors. By utilizing this conversion chart, researchers and students alike can efficiently convert between different units, ensuring accuracy and consistency in their scientific endeavors.
Units of Length
Length is a fundamental quantity that measures the distance between two points. In physics, the SI unit of length is the meter (m).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| meter (m) | 1 m | 1 |
| kilometer (km) | 1000 m | 0.001 km/m |
| centimeter (cm) | 0.01 m | 100 cm/m |
| millimeter (mm) | 0.001 m | 1000 mm/m |
| inch (in) | 0.0254 m | 39.37 in/m |
| foot (ft) | 0.3048 m | 3.281 ft/m |
Units of Mass
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| kilogram (kg) | 1 kg | 1 |
| gram (g) | 0.001 kg | 1000 g/kg |
| milligram (mg) | 0.000001 kg | 1,000,000 mg/kg |
| pound (lb) | 0.4536 kg | 2.205 lb/kg |
| ounce (oz) | 0.02835 kg | 35.27 oz/kg |
Units of Time
Time is a measure of the duration of an event or process. The SI unit of time is the second (s).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| second (s) | 1 s | 1 |
| minute (min) | 60 s | 0.0167 min/s |
| hour (h) | 3600 s | 0.000278 h/s |
| day (d) | 86400 s | 1.157 × 10^-5 d/s |
| year (yr) | 3.156 × 10^7 s | 3.171 × 10^-8 yr/s |
Units of Force
Force is a measure of the interaction between two objects. The SI unit of force is the newton (N).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| newton (N) | 1 N | 1 |
| kilonewton (kN) | 1000 N | 0.001 kN/N |
| pound-force (lbf) | 4.448 N | 0.2248 lbf/N |
| dyne (dyn) | 10^-5 N | 100,000 dyn/N |
Units of Energy
Energy is a measure of the capacity to do work. The SI unit of energy is the joule (J).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| joule (J) | 1 J | 1 |
| kilojoule (kJ) | 1000 J | 0.001 kJ/J |
| calorie (cal) | 4.184 J | 0.239 cal/J |
| British thermal unit (Btu) | 1055 J | 9.48 × 10^-4 Btu/J |
Units of Power
Power is a measure of the rate of doing work. The SI unit of power is the watt (W).
| Unit | SI Equivalent | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| watt (W) | 1 W | 1 |
| kilowatt (kW) | 1000 W | 0.001 kW/W |
| horsepower (hp) | 746 W | 0.00134 hp/W |
Benefits of Using a Conversion Chart
Utilizing a conversion chart for physics offers numerous advantages, including:
- Accuracy: Ensures precise conversion between different units, reducing potential errors in calculations.
- Consistency: Maintains uniformity in units and measurements, facilitating seamless collaboration between researchers.
- Time-saving: Eliminates the need for manual calculations, streamlining the scientific process.
- Improved communication: Facilitates effective communication among scientists, ensuring clarity and precision.
- Expanded applications: Enables researchers to venture into new areas of physics by providing a bridge between different units.
Applications of Conversion Charts
Conversion charts for physics find practical applications in a wide range of scientific fields, including:
- Engineering: Converting units of force, energy, and power in mechanical design and analysis.
- Astronomy: Transforming units of distance, time, and mass in astronomical observations.
- Medicine: Changing units of measurement for patient data, drug dosages, and medical equipment.
- Chemistry: Converting units of mass, volume, and concentration in chemical reactions.
- Environmental science: Translating units of energy, temperature, and pollution levels in environmental monitoring.
Conclusion
A conversion chart for physics is an indispensable tool for researchers and students, providing a comprehensive and accurate reference for converting between different units of measurement. By utilizing this chart, scientists can enhance the precision and consistency of their scientific work, fostering collaboration, and expanding their explorations into new areas of physics.