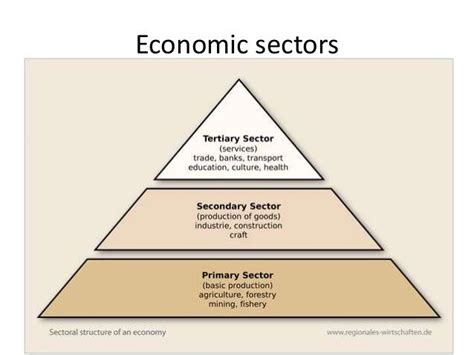
Understanding the Primary Sector
The primary sector, also known as the extractive sector, encompasses economic activities that directly involve the extraction and utilization of natural resources. These resources can include raw materials such as minerals, ores, agricultural products, livestock, fish, and timber. The primary sector plays a crucial role in providing essential commodities for human sustenance and economic development.

Key Activities of the Primary Sector
- Agriculture: This includes crop cultivation, livestock raising, forestry, and fishing. Agriculture provides food, fiber, and other raw materials for various industries.
- Mining: This involves the extraction of valuable minerals, metals, and other non-renewable resources from the earth’s crust.
- Logging and Forestry: These activities focus on the harvesting of timber and the management of forests for various purposes, including construction, paper production, and environmental conservation.
- Fishing: This sector includes commercial and recreational fishing operations that capture and harvest aquatic resources from oceans, lakes, and rivers.
Economic Significance of the Primary Sector
1. Employment: The primary sector is a significant employer in many developing countries, particularly in rural areas. It provides livelihoods for farmers, miners, loggers, and fisherfolk.
2. Food Security: Agriculture is crucial for ensuring food security by providing the world’s population with essential food supplies.
3. Raw Materials: The primary sector supplies raw materials for numerous industries, including construction, manufacturing, and energy production.
4. Economic Development: Extractive and agricultural activities can contribute to local, regional, and national economic development by generating revenue, creating jobs, and supporting other sectors.
Challenges and Trends in the Primary Sector
1. Climate Change: Agriculture and other primary sector activities are vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as droughts, floods, and sea level rise.
2. Land Use and Deforestation: Expanding agricultural practices and mining operations often lead to deforestation and land degradation, which can adversely impact ecosystems and biodiversity.
3. Sustainable Resource Management: Balancing economic exploitation with environmental conservation is a critical challenge for the primary sector.
Innovations and Advancements in the Primary Sector
1. Precision Agriculture: This involves using technology to optimize crop yields, reduce environmental impacts, and increase efficiency in agricultural practices.
2. Sustainable Mining: Techniques such as reclamation and waste reduction aim to minimize the environmental footprint of mining operations.
3. Aquaculture: This involves the controlled cultivation of aquatic species, offering a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional fishing practices.
Geographical Distribution of Primary Sector Activities
The primary sector is found in various geographic regions worldwide, with its distribution influenced by factors such as climate, soil conditions, and resource availability. Key primary sector regions include:
- Agriculture: Asia, Africa, and South America
- Mining: China, Australia, Canada
- Logging: Russia, Brazil, Indonesia
Tables
Table 1: Primary Sector Contribution to GDP
| Country | Primary Sector GDP (%) |
|---|---|
| India | 18.8 |
| United States | 2.0 |
| China | 10.6 |
Table 2: Employment in the Primary Sector
| Country | Primary Sector Employment (%) |
|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 45.4 |
| United Kingdom | 1.5 |
| Australia | 3.9 |
Table 3: Major Primary Sector Commodities
| Commodity | Share of Global Exports (%) |
|---|---|
| Oil | 16.9 |
| Wheat | 7.6 |
| Iron Ore | 5.7 |
Table 4: Challenges Facing the Primary Sector
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Climate Change | Reduced crop yields, water scarcity |
| Deforestation | Loss of biodiversity, soil degradation |
| Population Growth | Increased demand for food and resources |
FAQs
1. What is the difference between primary and secondary sector?
The primary sector involves extracting natural resources, while the secondary sector transforms these resources into finished or semi-finished products.
2. Why is the primary sector important?
The primary sector provides essential resources, such as food, energy, and raw materials, for human societies and economic growth.
3. What are some examples of primary sector jobs?
Farmers, miners, loggers, and fisherfolk are all employed in the primary sector.
4. How can the primary sector be made more sustainable?
Adopting precision agriculture, sustainable mining practices, and aquaculture can help reduce the environmental impacts of primary sector activities.
5. What are the major challenges facing the primary sector?
Climate change, deforestation, population growth, and technological advancements are prominent challenges.
6. What is the future of the primary sector?
Innovations, technology, and sustainable practices will continue to shape the future of the primary sector to meet the growing demand for resources while minimizing environmental impacts.