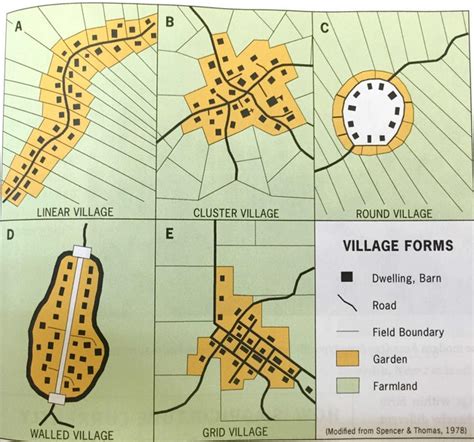
Land use refers to the various ways in which humans utilize land for different purposes. Understanding land use is crucial in AP Human Geography as it provides insights into how societies shape and are shaped by their environment.

Land Use Patterns and Trends
Urbanization: The growth of cities is a defining trend in land use across the globe. By 2050, it is estimated that over 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas. This urbanization process leads to increased land conversion for residential, commercial, and industrial uses.
Agricultural Expansion: Agriculture remains a significant land use, particularly in developing countries. However, the demand for food production is expected to increase by 70% by 2050. This has led to the expansion of agricultural land, often at the expense of forests and other natural ecosystems.
Environmental Degradation: Land use can have significant environmental impacts. Deforestation, for example, contributes to climate change, loss of biodiversity, and soil erosion. Urban development can also lead to air pollution, noise pollution, and water scarcity.
Factors Influencing Land Use
- Economic Factors: Economic activities, such as agriculture, industry, and tourism, drive land use patterns.
- Social Factors: Population growth, migration, and cultural preferences influence land use decisions.
- Political Factors: Government policies, such as zoning laws and land-use planning, shape how land is utilized.
- Environmental Factors: The physical characteristics of land, including soil quality, water availability, and topography, affect land use options.
Urban Land Use
Residential Land Use: This includes areas designated for housing, such as single-family homes, apartments, and condominiums.
Commercial Land Use: This refers to areas used for businesses, such as retail stores, offices, and restaurants.
Industrial Land Use: This includes areas used for manufacturing and other industrial activities.
Transportation Infrastructure: This includes roads, highways, railroads, and airports.
Rural Land Use
Agricultural Land Use: This includes areas used for farming, livestock production, and forestry.
Natural Land Use: This includes areas designated for conservation, such as parks, forests, and wetlands.
Recreational Land Use: This includes areas used for outdoor recreation, such as hiking, camping, and fishing.
Land Use Planning
Zoning: Zoning laws establish regulations and restrictions on land use within specific areas.
Land-Use Planning: This involves developing comprehensive plans to guide future land use development and minimize negative impacts.
Smart Growth: This approach promotes sustainable and compact urban development, reducing sprawl and preserving natural areas.
Key Impacts of Land Use
- Economic Impacts: Land use can affect economic development, job creation, and property values.
- Social Impacts: Land use can influence community livability, access to services, and social well-being.
- Environmental Impacts: Land use can have significant consequences for ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources.
Sustainable Land Use Practices
- Urban Greening: Increasing green spaces in urban areas can reduce air pollution, improve water quality, and promote biodiversity.
- Mixed-Use Development: Combining different land uses within a single development can reduce traffic congestion, promote walkability, and foster social interaction.
- Brownfield Redevelopment: Redeveloping abandoned or contaminated sites can reduce sprawl and promote economic revitalization.
- Precision Agriculture: Using technology to optimize agricultural production can reduce environmental impacts and increase yields.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and crops in agricultural systems can provide multiple benefits, such as carbon sequestration, soil improvement, and biodiversity conservation.
Conclusion
Land use is a complex and dynamic aspect of AP Human Geography. Understanding land use patterns, trends, and influences is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable development. By adopting sustainable land use practices, we can mitigate environmental impacts, enhance community well-being, and ensure the long-term viability of our planet.
Tables
-
Table 1: Urban Land Use Categories
| Land Use Category | Description |
|—|—|
| Residential | Areas designated for housing |
| Commercial | Areas used for businesses |
| Industrial | Areas used for manufacturing and other industrial activities |
| Transportation Infrastructure | Roads, highways, railroads, and airports | -
Table 2: Rural Land Use Categories
| Land Use Category | Description |
|—|—|
| Agricultural | Areas used for farming, livestock production, and forestry |
| Natural | Areas designated for conservation, such as parks, forests, and wetlands |
| Recreational | Areas used for outdoor recreation, such as hiking, camping, and fishing | -
Table 3: Impacts of Land Use
| Impact | Description |
|—|—|
| Economic | Affects economic development, job creation, and property values |
| Social | Influences community livability, access to services, and social well-being |
| Environmental | Consequences for ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources | -
Table 4: Sustainable Land Use Practices
| Practice | Description |
|—|—|
| Urban Greening | Increasing green spaces in urban areas |
| Mixed-Use Development | Combining different land uses within a single development |
| Brownfield Redevelopment | Redeveloping abandoned or contaminated sites |
| Precision Agriculture | Using technology to optimize agricultural production |
| Agroforestry | Integrating trees and crops in agricultural systems |