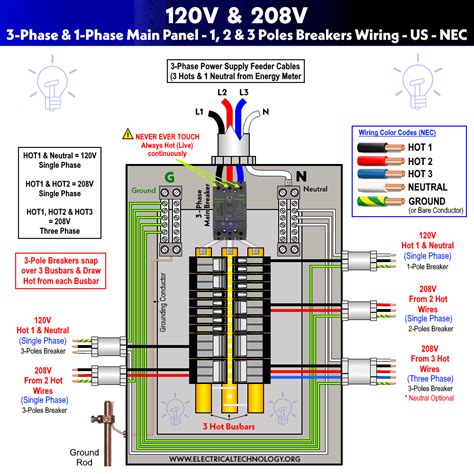
In the realm of electrical distribution, the 3 phase sub panel reigns supreme as the unsung hero, providing efficient and reliable power to a vast array of electrical systems. Whether it’s powering industrial machinery, commercial buildings, or even residential dwellings, this indispensable electrical component plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of any electrical infrastructure.

Understanding 3 Phase Sub Panels
A 3 phase sub panel is a type of electrical panel that receives power from a 3 phase main electrical panel and distributes it to various circuits within a smaller area, such as a workshop, office space, or apartment. It consists of switches, circuit breakers, and other electrical components that protect and control the flow of electricity to specific outlets, appliances, and equipment.
Benefits of 3 Phase Sub Panels
3 phase sub panels offer a myriad of benefits, including:
- Increased Power Capacity: 3 phase power provides significantly greater power capacity compared to single phase power, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications that require high power consumption.
- Efficiency and Stability: 3 phase systems are more efficient than single phase systems, as they minimize power losses and provide more stable voltage levels, ensuring consistent and reliable power delivery.
- Reduced Voltage Drops: The use of 3 phase sub panels minimizes voltage drops compared to single phase systems, especially over longer distances, improving power quality and reducing the risk of equipment damage.
- Flexibility and Expandability: Sub panels allow for flexible power distribution and easy expansion, facilitating the addition of circuits and equipment as needed.
Applications of 3 Phase Sub Panels
The versatility of 3 phase sub panels enables them to be utilized in a wide range of applications, including:
- Industrial Facilities: Powering machinery, conveyors, pumps, and other industrial equipment that require high power consumption.
- Commercial Buildings: Distributing power to lighting systems, HVAC systems, elevators, and other critical infrastructure in office buildings, shopping malls, and hospitals.
- Residential Dwellings: Providing power to large appliances, electric vehicle charging stations, and other high-power equipment in homes and apartments.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Integrating solar and wind energy systems into the electrical grid, facilitating reliable and efficient power distribution.
Pain Points and Motivations
Despite their advantages, 3 phase sub panels can also present some challenges and pain points:
- Cost and Complexity: 3 phase sub panels and associated wiring can be more expensive and complex to install compared to single phase systems.
- Availability of 3 Phase Power: Not all locations have readily available access to 3 phase power, which may limit the use of sub panels in certain areas.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Regular maintenance and occasional upgrades may be necessary to ensure optimal performance and safety of 3 phase sub panels.
However, the motivations for utilizing 3 phase sub panels often outweigh these pain points, particularly in applications where high power capacity, efficiency, stability, and flexibility are paramount.
Effective Strategies for 3 Phase Sub Panel Installation
To ensure successful and safe installation of 3 phase sub panels, consider the following effective strategies:
- Consult with a Qualified Electrician: Hiring a licensed electrician is crucial for proper installation, compliance with electrical codes, and ensuring the safety of your electrical system.
- Assess Power Requirements: Determine the specific power requirements of the equipment and appliances that will be connected to the sub panel to ensure it has sufficient capacity.
- Plan for Future Expansion: Consider potential future power needs and incorporate additional circuits or capacity into the sub panel design to accommodate future growth.
- Use High-Quality Components: Invest in reputable electrical components such as switches, circuit breakers, and wiring to minimize the risk of malfunctions and ensure durability.
FAQs on 3 Phase Sub Panels
Frequently asked questions regarding 3 phase sub panels include:
- What is the difference between 3 phase and single phase power? 3 phase power provides greater power capacity and efficiency compared to single phase power, which is more commonly used in residential applications.
- Do I need a 3 phase sub panel for my home? It depends on the power requirements of your appliances and equipment. Homes with high-power consumption may benefit from the increased capacity and efficiency of 3 phase power.
- How much does it cost to install a 3 phase sub panel? The cost varies depending on the size, complexity, and materials used. Consult with a qualified electrician for an accurate estimate.
- How often should I maintain my 3 phase sub panel? Regular maintenance, including visual inspections, testing, and cleaning, is recommended every 5-7 years or more frequently if necessary.
- What are the safety precautions for working with 3 phase power? Always wear proper protective gear, follow electrical safety codes, and consult with a qualified electrician for any maintenance or repair work.
- What if I don’t have access to 3 phase power? In areas without 3 phase power availability, consider alternative power sources such as generators or inverters to meet high power demands.
Generating New Applications for 3 Phase Sub Panels
To further expand the applications of 3 phase sub panels, consider the following creative approaches:
- Smart Energy Management: Integrate 3 phase sub panels with smart energy management systems to optimize power consumption, reduce energy costs, and improve system efficiency.
- Microgrids and Off-Grid Systems: Utilize 3 phase sub panels to distribute power generated from renewable energy sources in microgrids and off-grid systems, providing reliable and sustainable electricity.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: Incorporate 3 phase sub panels into electric vehicle charging stations to provide faster and more efficient charging capabilities for electric vehicles.
- Data Center Power Distribution: Design 3 phase sub panels specifically for data center power distribution to meet the high power density requirements and ensure continuous uptime for critical IT infrastructure.
Conclusion
3 phase sub panels are essential components in electrical distribution systems, providing increased power capacity, efficiency, and stability for a wide range of electrical applications. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and effective strategies for installation of 3 phase sub panels, businesses, organizations, and individuals can harness the power of 3 phase electricity to meet their evolving electrical needs and achieve optimal performance.
| Feature | 3 Phase Power | Single Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Power Capacity | Higher | Lower |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Voltage Stability | More stable | Less stable |
| Voltage Drops | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Industrial machinery, commercial buildings, large appliances | Residential homes, small appliances |
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Industrial Facilities | Powering machinery, conveyors, pumps |
| Commercial Buildings | Distributing power to lighting systems, HVAC systems |
| Residential Dwellings | Providing power to large appliances, electric vehicle charging stations |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Integrating solar and wind energy systems into the electrical grid |
| Pain Points | Motivations |
|---|---|
| Cost and Complexity | Increased power capacity, efficiency, and stability |
| Availability of 3 Phase Power | Accessibility to higher power requirements |
| Maintenance and Upgrades | Reliability and safety |
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Consult with a Qualified Electrician | Ensure proper installation and compliance with electrical codes |
| Assess Power Requirements | Determine the specific power needs of connected equipment |
| Plan for Future Expansion | Accommodate potential growth in power consumption |
| Use High-Quality Components | Minimize risk of malfunctions and ensure durability |