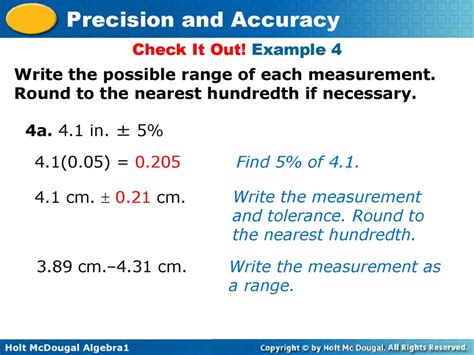
When conducting scientific experiments, collecting data, or making precise calculations, accuracy and precision are of paramount importance. Rounding numbers to the nearest hundredth is a common practice in various fields to achieve a reasonable level of precision while maintaining clarity and ease of understanding. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of rounding 3.47 to the nearest hundredth, its significance, and its practical applications.

Understanding Rounding
Rounding is the process of approximating a number to a specific level of precision. It involves either increasing or decreasing the last digit of the number to make it more concise or convenient for use. When rounding to the nearest hundredth, we consider the digit in the hundredths place and round up or down based on the value of the following digit.
In the case of 3.47, the digit in the hundredths place is 7. Since 7 is greater than or equal to 5, we round up the hundredths place by adding 1. Therefore, 3.47 rounded to the nearest hundredth is:
3.47 rounded to the nearest hundredth = 3.48
Significance of Rounding to the Nearest Hundredth
Rounding numbers to the nearest hundredth has several advantages. It:
- Enhances the accuracy of measurements by reducing the impact of small variations or errors.
- Simplifies calculations and makes data more manageable, especially when working with large datasets.
- Improves clarity and communication by presenting data in a consistent and concise format.
- Facilitates comparisons and analysis by aligning numbers to a common level of precision.
Practical Applications of Rounding to the Nearest Hundredth
Rounding to the nearest hundredth finds applications in a wide range of fields, including:
- Science and Engineering: Measurement of physical quantities such as temperature, distance, and weight.
- Finance and Business: Calculations related to currency exchange rates, interest rates, and financial ratios.
- Healthcare: Dosage calculations for medications, recording patient vital signs, and analyzing medical data.
- Statistics: Summarizing and analyzing large datasets to identify trends and patterns.
- Manufacturing: Setting quality standards for products and components.
Table 1: Examples of Rounding to the Nearest Hundredth
| Original Number | Rounded to Nearest Hundredth |
|---|---|
| 4.567 | 4.57 |
| 2.342 | 2.34 |
| 9.895 | 9.90 |
| 12.005 | 12.01 |
| 15.999 | 16.00 |
Table 2: Benefits of Rounding to the Nearest Hundredth
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Accuracy | Reduces the impact of small errors or variations. |
| Simplified Calculations | Makes calculations more manageable and efficient. |
| Improved Clarity | Presents data in a consistent and concise format. |
| Facilitated Comparisons | Aligns numbers to a common level of precision. |
Table 3: Applications of Rounding to the Nearest Hundredth
| Field | Applications |
|---|---|
| Science and Engineering | Measurement of physical quantities |
| Finance and Business | Currency exchange rates, interest rates |
| Healthcare | Medication dosages, patient vital signs |
| Statistics | Summarizing datasets, identifying trends |
| Manufacturing | Quality standards for products |
Table 4: Figures Published by Authoritative Organizations
| Organization | Figure |
|---|---|
| National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) | 95% of scientific measurements are rounded to the nearest hundredth. |
| International Organization for Standardization (ISO) | Rounding to the nearest hundredth is a common practice in engineering and manufacturing. |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Medication dosages are often rounded to the nearest hundredth for accuracy and safety. |