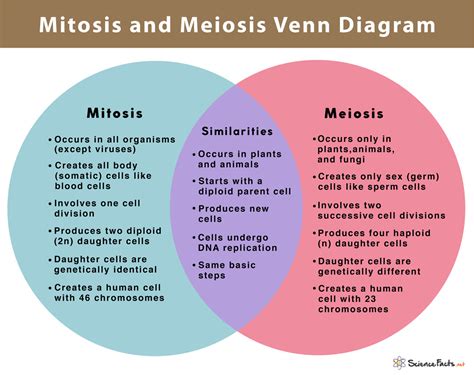
Introduction:

Meiosis and mitosis are essential biological processes that contribute significantly to the genetic diversity and propagation of life on Earth. While they share many fundamental principles, these processes exhibit distinct characteristics that cater to specific biological functions. This article explores two notable similarities between meiosis and mitosis, highlighting their shared mechanisms and significance in cellular reproduction.
1. Chromosomal Replication:
-
Description:
- Meiosis and mitosis both initiate with chromosomal replication, where the DNA in each chromosome is duplicated, resulting in identical sister chromatids.
- In meiosis, this process occurs before Meiosis I, while in mitosis, it precedes cell division.
-
Significance:
- Chromosomal replication ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material, maintaining genetic integrity.
- It also serves as a preparatory step for the chromosome segregation that follows in both meiosis and mitosis.
2. Phase of Cytokinesis:
-
Description:
- Meiosis and mitosis conclude with cytokinesis, the physical division of the cell into daughter cells.
- In meiosis, cytokinesis occurs twice, following Meiosis I and Meiosis II, producing four haploid daughter cells.
- In mitosis, cytokinesis separates the two daughter cells with identical genetic content.
-
Significance:
- Cytokinesis ensures that the daughter cells inherit their respective set of chromosomes, ensuring proper development and genetic inheritance.
- It completes the cell division process, distributing the replicated genetic material and forming new individual cells.
Distinctive Features:
While meiosis and mitosis share these similarities, they also possess distinct features that differentiate their roles in cellular reproduction:
- Number of Daughter Cells: Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells, while mitosis produces two diploid daughter cells.
- Genetic Variation: Meiosis generates genetically diverse daughter cells through crossing-over and independent assortment, while mitosis maintains the genetic identity of daughter cells.
- Purpose: Meiosis is specialized for sexual reproduction, producing gametes (eggs and sperm), while mitosis is primarily involved in asexual reproduction and cell growth.
Applications:
The understanding of meiosis and mitosis has far-reaching applications in various fields:
- Genetics: Comprehending these processes helps researchers study genetic inheritance and variation.
- Medicine: Misregulation of meiosis and mitosis can contribute to genetic disorders and certain types of cancer.
- Agriculture: Knowledge of chromosomal replication and cytokinesis aids in plant and animal breeding for improved traits.
Tips and Tricks:
- To distinguish between meiosis and mitosis, remember that meiosis involves two cell divisions (Meiosis I and II), while mitosis involves only one.
- The haploid daughter cells produced by meiosis have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while the diploid daughter cells produced by mitosis have the same number.
- Visual aids such as diagrams and animations can enhance the understanding of these complex processes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Do not confuse meiosis with mitosis as they serve distinct functions in cellular reproduction.
- Do not assume that all daughter cells produced by meiosis are identical. Genetic variation is a fundamental aspect of meiosis.
- Avoid using imprecise language. Meiosis and mitosis are well-defined biological processes with specific characteristics.
FAQs:
-
What is the main difference between meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: Meiosis produces haploid cells (with half the number of chromosomes) through two cell divisions, while mitosis produces diploid cells (with the same number of chromosomes) through one cell division. -
Why is chromosomal replication important in both meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: Chromosomal replication ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material, maintaining genetic integrity. -
How does cytokinesis differ in meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: In meiosis, cytokinesis occurs twice, separating the chromosomes into four haploid daughter cells, while in mitosis, it occurs once, resulting in two diploid daughter cells. -
What are the practical applications of understanding meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: These processes have implications in genetics, medicine, and agriculture, enabling the study of genetic variation, diagnosis and treatment of genetic disorders, and improvement of plant and animal breeding practices. -
How can I improve my understanding of meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: Use diagrams, animations, and read scientific articles on these topics. Consult with experts in the field for further clarification. -
What is a key misconception about meiosis?
Answer: A common misconception is that meiosis always produces genetically identical daughter cells. However, crossing-over and independent assortment during meiosis lead to genetic variation in the daughter cells. -
What are the consequences of abnormal meiosis or mitosis?
Answer: Errors in these processes can result in genetic disorders, developmental defects, and certain types of cancer. -
How can I further explore the complexities of meiosis and mitosis?
Answer: Engage in scientific discussions, attend conferences, and delve into research articles and textbooks to gain in-depth knowledge of these fundamental biological processes.
Conclusion:
Meiosis and mitosis, despite their unique characteristics, share the fundamental mechanisms of chromosomal replication and cytokinesis. Understanding these similarities provides a foundation for comprehending the intricate world of cell division and its implications in various fields. By delving deeper into the nuances of these processes, we unlock the potential for advancements in genetics, medicine, and agriculture, enabling us to harness their power for the benefit of humanity.