Introduction
The AP US Government exam is a rigorous test that requires students to possess a comprehensive understanding of the principles and structure of the American government and its political system. The 2.9 unit of the exam focuses specifically on the principles of American democracy, including the founding principles, constitutional principles, and the structure of the federal government.

Founding Principles
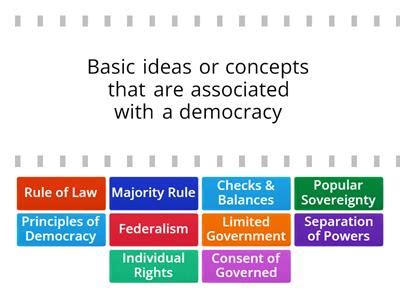
The founding principles of American democracy are the fundamental ideas upon which the nation was founded. These principles include:
- Natural Rights: The belief that individuals have inherent rights, such as life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness, that are not granted by the government.
- Popular Sovereignty: The belief that the government derives its power from the consent of the governed.
- Limited Government: The belief that the government’s authority should be limited to protect the rights of individuals and promote the common good.
These principles were heavily influenced by the Enlightenment philosophers, such as John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and are enshrined in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution.
Constitutional Principles
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the land and establishes the framework for the federal government. The constitutional principles that govern the American democracy include:
- Separation of Powers: The division of government power among three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
- Checks and Balances: The system in which each branch of government has the ability to check the powers of the other branches, thereby preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful.
- Federalism: The division of power between the national government and the state governments.
These principles ensure that no single branch of government has unchecked authority and that the rights of citizens are protected.
Structure of the Federal Government
The federal government of the United States is divided into three branches:
- Legislative Branch: The bicameral Congress, which consists of the Senate and the House of Representatives, is responsible for making laws.
- Executive Branch: The President, who is responsible for enforcing laws and conducting foreign policy.
- Judicial Branch: The Supreme Court and lower federal courts, which are responsible for interpreting laws and settling disputes.
Each branch has its own powers and responsibilities, and they work together to ensure that the government operates effectively.
Principles in Practice
The principles of American democracy are not only abstract ideals but also practical realities that shape the functioning of the government. For example:
- Natural Rights: The Bill of Rights in the Constitution protects individual rights, such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly.
- Popular Sovereignty: Elections allow citizens to choose their representatives and participate in the governing process.
- Limited Government: The Constitution limits the government’s authority to prevent it from infringing on individual rights.
Challenges to American Democracy
While the principles of American democracy are strong and enduring, they have also faced challenges over the years. These challenges include:
- Political Polarization: The increasing divide between the two major political parties, which can make it difficult to find common ground and solve problems.
- Erosion of Trust: Declining trust in government institutions and elected officials.
- Threats to Civil Liberties: Attempts to limit or restrict individual rights, such as freedom of speech or the right to privacy.
Preserving American Democracy
Preserving American democracy requires ongoing vigilance and active participation from citizens. Strategies for preserving democracy include:
- Voting and Civic Engagement: Participating in elections, serving on juries, and advocating for causes that promote democratic principles.
- Media Literacy: Understanding the role of the media in society and being able to critically evaluate information.
- Education: Learning about the history, principles, and structure of American democracy.
2.9 AP US Government: Tables
Table 1: Principles of American Democracy
| Principle | Description | Key Documents |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Rights | Individuals have inherent rights, such as life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness | Declaration of Independence |
| Popular Sovereignty | Government derives its power from the consent of the governed | Declaration of Independence, Constitution |
| Limited Government | Government’s authority should be limited to protect individual rights and promote the common good | Constitution, Bill of Rights |
Table 2: Constitutional Principles that Govern American Democracy
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Separation of Powers | Power is divided among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches |
| Checks and Balances | Each branch can check the powers of the other branches |
| Federalism | Power is divided between the national and state governments |
Table 3: Structure of the Federal Government
| Branch | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Legislative (Congress) | Makes laws |
| Executive (President) | Enforces laws, conducts foreign policy |
| Judicial (Supreme Court, Lower Courts) | Interprets laws, settles disputes |
Table 4: Challenges to American Democracy and Strategies for Preserving It
| Challenge | Strategies for Preserving Democracy |
|---|---|
| Political Polarization | Promote dialogue and compromise, encourage bipartisanship |
| Erosion of Trust | Increase transparency and accountability, restore faith in institutions |
| Threats to Civil Liberties | Advocate for individual rights, challenge restrictions, educate about importance of civil liberties |
Quiz
-
Which of the following is a founding principle of American democracy?
- Limited Government
- Universal Healthcare
- Divine Right of Kings
- Totalitarianism
-
Which constitutional principle prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful?
- Separation of Powers
- Checks and Balances
- Federalism
- Electoral College
-
Which branch of government is responsible for making laws?
- Executive
- Legislative
- Judicial
- Cabinet
-
Which of the following is a challenge facing American democracy?
- Political Polarization
- Climate Change
- Economic Inequality
- All of the above
Conclusion
The principles of American democracy are the foundation upon which the nation was founded and have endured for over two centuries. These principles ensure that individual rights are protected, that government is accountable to the people, and that the nation remains a beacon of freedom and opportunity.