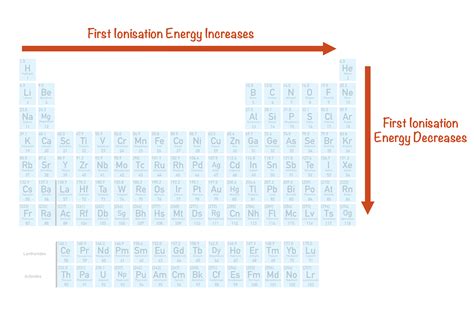
The first ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state. It is a measure of the strength of the attractive force between the nucleus and the electron. The higher the first ionization energy, the stronger the attractive force is and the more difficult it is to remove an electron.

The following table shows the first ionization energies of the elements in the periodic table:
| Element | Symbol | First Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1312 |
| Helium | He | 2372 |
| Lithium | Li | 520 |
| Beryllium | Be | 900 |
| Boron | B | 801 |
| Carbon | C | 1086 |
| Nitrogen | N | 1402 |
| Oxygen | O | 1314 |
| Fluorine | F | 1680 |
| Neon | Ne | 2081 |
| Sodium | Na | 496 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 738 |
| Aluminum | Al | 578 |
| Silicon | Si | 786 |
| Phosphorus | P | 1012 |
| Sulfur | S | 1000 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 1251 |
| Argon | Ar | 1521 |
| Potassium | K | 419 |
| Calcium | Ca | 590 |
| Gallium | Ga | 579 |
| Germanium | Ge | 762 |
| Arsenic | As | 947 |
| Selenium | Se | 941 |
| Bromine | Br | 1140 |
| Krypton | Kr | 1351 |
| Rubidium | Rb | 403 |
| Strontium | Sr | 549 |
| Yttrium | Y | 600 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 663 |
| Niobium | Nb | 652 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 684 |
| Technetium | Tc | 702 |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 720 |
| Rhodium | Rh | 720 |
| Palladium | Pd | 804 |
| Silver | Ag | 731 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 867 |
| Indium | In | 558 |
| Tin | Sn | 709 |
| Antimony | Sb | 834 |
| Tellurium | Te | 869 |
| Iodine | I | 1008 |
| Xenon | Xe | 1170 |
| Cesium | Cs | 375 |
| Barium | Ba | 503 |
| Lanthanum | La | 538 |
| Cerium | Ce | 534 |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 527 |
| Neodymium | Nd | 533 |
| Promethium | Pm | 540 |
| Samarium | Sm | 544 |
| Europium | Eu | 547 |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 593 |
| Terbium | Tb | 566 |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 573 |
| Holmium | Ho | 581 |
| Erbium | Er | 589 |
| Thulium | Tm | 597 |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 603 |
| Lutetium | Lu | 524 |
| Hafnium | Hf | 659 |
| Tantalum | Ta | 700 |
| Tungsten | W | 770 |
| Rhenium | Re | 760 |
| Osmium | Os | 840 |
| Iridium | Ir | 880 |
| Platinum | Pt | 870 |
| Gold | Au | 890 |
| Mercury | Hg | 1007 |
| Thallium | Tl | 589 |
| Lead | Pb | 716 |
| Bismuth | Bi | 703 |
| Polonium | Po | 812 |
| Astatine | At | 920 |
| Radon | Rn | 1037 |
| Francium | Fr | 380 |
| Radium | Ra | 509 |
| Actinium | Ac | 499 |
| Thorium | Th | 587 |
| Protactinium | Pa | 568 |
| Uranium | U | 598 |
| Neptunium | Np | 605 |
| Plutonium | Pu | 585 |
| Americium | Am | 578 |
| Curium | Cm | 581 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 601 |
| Californium | Cf | 608 |
| Einsteinium | Es | 619 |
| Fermium | Fm | 627 |
| Mendelevium | Md | 635 |
| Nobelium | No | 642 |
| Lawrencium | Lr | 640 |
| Rutherfordium | Rf | 644 |
| Dubnium | Db | 656 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 661 |
| Bohrium | Bh | 665 |
| Hassium | Hs | 670 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 675 |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 681 |
| Roentgenium | Rg | 687 |
| Copernicium | Cn | 693 |
| Nihonium | Nh | 697 |
| Flerovium | Fl | 702 |
| Moscovium | Mc | 709 |
| Livermorium | Lv | 715 |
| Tennessine | Ts | 720 |
| Oganesson | Og | 725 |
Factors Affecting First Ionization Energy
The first ionization energy of an element is affected by a number of factors, including:
- Atomic number: The first ionization energy generally increases across a period (row) of the periodic table from left to right. This is because the effective nuclear charge (the net positive charge experienced by an electron in an atom) increases across a period.
- Atomic radius: The first ionization energy generally decreases down a group (column) of the periodic table from top to bottom. This is because the atomic radius increases down a group, which means that the valence electrons are further from the nucleus and are less strongly attracted to it.
- Electron configuration: The first ionization energy is also affected by the electron configuration of the atom. Atoms with a half-filled or completely filled valence shell are more stable and have higher first ionization energies.
Applications of First Ionization Energy
The first ionization energy of an element is a useful property that can be used in a variety of applications, including:
- Predicting chemical reactivity: The first ionization energy can be used to predict the chemical reactivity of an element. Elements with low first ionization energies are more likely to be reactive and form bonds with other elements.
- Understanding atomic structure: The first ionization energy can be used to understand the atomic structure of an element. It can provide information about the number of valence electrons and the energy levels of the electrons.
- Developing materials: The first ionization energy can be used to develop new materials with specific properties. For example, materials with high first ionization energies are more resistant to corrosion and oxidation.
Conclusion
The first ionization energy is a fundamental property of an element that can be used to understand its chemical reactivity, atomic structure, and potential applications. By understanding the factors that affect first ionization energy, we can gain insights into the behavior of elements and develop new materials with specific properties.
Additional Resources
Tables
Table 1: First Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) of the Alkali Metals
| Element | Symbol | First Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Li | 520 |
| Sodium | Na | 496 |
| Potassium | K | 419 |
| Rubidium | Rb | 403 |
| Cesium | Cs | 375 |
| Francium | Fr | 380 |
Table 2: First Ionization Energy (kJ