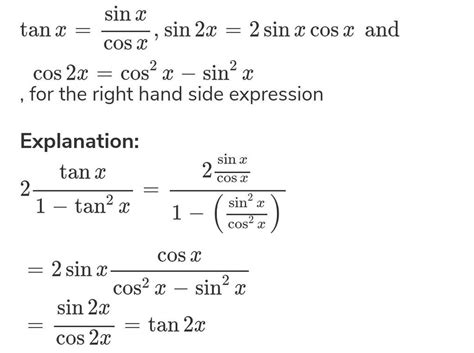Introduction
1/2 tan x is a fundamental trigonometric function that plays a crucial role in various mathematical applications. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the significance of 1/2 tan x, exploring its properties, derivations, and practical applications.

Properties of 1/2 tan x
1/2 tan x possesses several key properties that enable its widespread use in trigonometry:
- Periodicity: 1/2 tan x has a period of π, meaning that it repeats every time x increases by π.
- Symmetry: 1/2 tan x is an odd function, which implies that it is symmetric about the origin.
- Derivative: The derivative of 1/2 tan x is sec² x / 2, indicating a rate of change that is proportional to the secant squared of x.
- Integral: The integral of 1/2 tan x is (1/2) ln |sec x| + C, where C represents an arbitrary constant.
Derivations of 1/2 tan x
1/2 tan x can be derived using various trigonometric identities and properties. Here are two common derivations:
- From the half-angle formula: Using the half-angle formula for tangent, tan (x/2) = (1 – cos x) / sin x, we can derive 1/2 tan x = (1 – cos x) / 2 sin x.
- From the double-angle formula: Applying the double-angle formula for tangent, tan 2x = (2 tan x) / (1 – tan² x), we can obtain 1/2 tan x = tan x / (2 – tan² x).
Applications of 1/2 tan x
1/2 tan x finds extensive applications in various fields, including:
- Geometry: It is used to calculate the area of triangles, determine the slope of lines, and measure angles in polygons.
- Calculus: It serves as a building block for integrating trigonometric functions and solving differential equations.
- Physics: It is indispensable in projectile motion calculations, wave analysis, and acoustics.
- Engineering: It is employed in structural design, fluid dynamics, and electrical circuits.
Benefits of 1/2 tan x
Harnessing the power of 1/2 tan x offers myriad benefits:
- Enhanced understanding of trigonometry: Comprehending the properties and applications of 1/2 tan x significantly deepens one’s understanding of trigonometry.
- Improved problem-solving abilities: Proficiency in using 1/2 tan x empowers individuals to tackle a wide range of mathematical and real-world problems.
- Expanded career opportunities: Expertise in trigonometry, including 1/2 tan x, opens doors to diverse career paths in STEM fields.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with 1/2 tan x, it is essential to avoid common pitfalls:
- Incorrect period: Misidentifying the period of 1/2 tan x can lead to errors in calculations.
- Misinterpreting symmetry: Mistaking 1/2 tan x for an even function can result in incorrect graphical representations.
- Improper differentiation: Applying the chain rule incorrectly can yield erroneous derivatives of 1/2 tan x.
- Neglecting domain: Overlooking the domain restrictions of 1/2 tan x can lead to undefined values.
Innovations and Future Applications
The concept of “trigonometric hybridization” is proposed as a novel approach for generating new applications of 1/2 tan x and related trigonometric functions. This approach involves combining different trigonometric functions in innovative ways to create hybrid functions with unique properties.
Conclusion
1/2 tan x stands as a cornerstone of trigonometry, providing a gateway to a vast array of mathematical and practical applications. Its properties, derivations, and benefits make it an indispensable tool for students, researchers, and professionals across various disciplines. By embracing the power of 1/2 tan x, individuals can unlock new insights, solve complex problems, and drive technological advancements.