Introduction

The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It is a powerful tool for understanding the chemical behavior of elements and their applications in various fields.
History of the Periodic Table
The concept of a periodic table was first proposed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Mendeleev arranged the elements known at the time in order of increasing atomic mass, and grouped them according to their chemical properties. This arrangement revealed a pattern of recurring properties, known as periodicity.
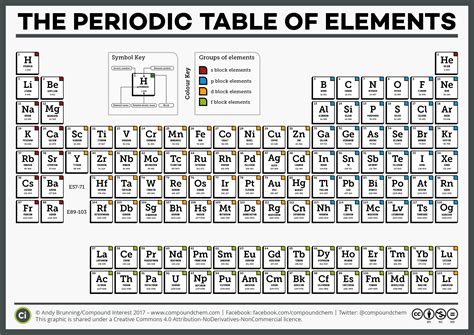
Over the years, the periodic table has been expanded and refined as new elements were discovered. The modern periodic table contains 118 elements, arranged in 18 columns (groups) and 7 rows (periods).
Structure of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is organized into the following structural elements:
- Groups: The vertical columns represent groups of elements with similar chemical properties. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
- Periods: The horizontal rows represent periods of elements with the same number of electron shells.
- Blocks: The periodic table is further divided into blocks based on the orbital where the valence electrons are located: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
Element Properties
The position of an element in the periodic table provides valuable information about its properties:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus, which determines the element’s identity.
- Atomic Weight: The average mass of the element’s atoms,考虑到the element’s different isotopes.
- Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons in the energy levels of the atom.
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
- Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
- Atomic Radius: The distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.
Periodic Trends
Several periodic trends can be observed in the properties of elements across the periodic table:
- Atomic Radius: Decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom down a group.
- Electronegativity: Increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom down a group.
- Ionization Energy: Increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom down a group.
- Metallic Character: Increases from top to bottom down a group and decreases from left to right across a period.
- Nonmetallic Character: Exhibits the opposite trend of metallic character.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table finds numerous applications in various fields:
- Chemical Engineering: Predicts the properties and reactivity of chemical compounds.
- Materials Science: Guides the development of new materials with specific properties.
- Medicine: Helps in understanding drug interactions and designing new therapies.
- Environmental Science: Aids in understanding the behavior of pollutants and designing remediation strategies.
- Education: Provides a structured framework for teaching chemistry and understanding chemical concepts.
Tips and Tricks for Using the Periodic Table
- Remember the mnemonic devices for group names (e.g., “Helium Has No Peers” for group 18).
- Use the periodic table to predict the properties of unknown elements based on their position.
- Identify patterns and trends in the table to make connections between different elements.
- Consult reliable sources to verify information and expand your knowledge about specific elements.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: Why is the periodic table important?
A: The periodic table provides a comprehensive organization of chemical elements, allowing for the prediction of properties, reactivity, and applications in various fields. -
Q: How can I use the periodic table to identify an element?
A: Determine the atomic number, which is the unique identifier for each element. Refer to the atomic number in the periodic table to find the corresponding element. -
Q: What is electronegativity?
A: Electronegativity measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom down a group. -
Q: What role does the periodic table play in environmental science?
A: The periodic table assists in understanding the behavior of pollutants, their interactions with the environment, and the development of strategies for pollution control and remediation.
Conclusion
The periodic table is a fundamental tool for understanding chemical elements and their behavior. Its organization, trends, and applications make it an indispensable resource in various fields. By mastering the periodic table, students, researchers, and professionals can gain valuable insights into the chemical world and drive advancements in science and technology.