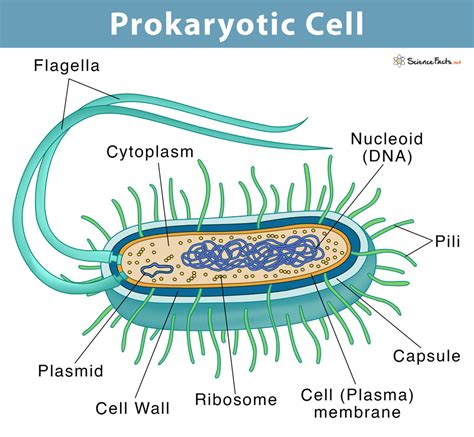
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and oldest type of cell, lacking a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life.Bacteria are the most common type of prokaryote, and they are found in a wide variety of environments, including soil, water, and air. They are responsible for a wide range of processes, such as decomposition, fermentation, and nitrogen fixation.Archaea are less common than bacteria, and they are found in more extreme environments, such as hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and salt lakes. They are able to survive in these environments thanks to their unique cell structure, which includes a cell wall made of a different type of sugar than that found in bacteria.

Here are some examples of prokaryotic cells:
-
Bacteria
-
Archaea
Here are some examples of eukaryotic cells:
- Plants
- Animals
- Fungi
- Protists
Table 1: Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic cells | Eukaryotic cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5 µm | 10-100 µm |
| Shape | Spherical, rod-shaped, or spiral | Irregular |
| Nucleus | No nucleus | Nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts |
| Ribosomes | 70S ribosomes | 80S ribosomes |
| Cell wall | Cell wall made of peptidoglycan | Cell wall made of cellulose or chitin |
| Flagella | Flagella made of a single protein | Flagella made of a complex of proteins |
Table 2: Examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms
| Organism | Type of cell |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic |
| Archaea | Prokaryotic |
| Plants | Eukaryotic |
| Animals | Eukaryotic |
| Fungi | Eukaryotic |
| Protists | Eukaryotic |
Table 3: Applications of prokaryotic cells
| Application | Organism |
|---|---|
| Decomposition | Bacteria |
| Fermentation | Bacteria |
| Nitrogen fixation | Bacteria |
| Bioremediation | Bacteria |
| Food production | Bacteria |
| Medicine | Bacteria |
Table 4: Challenges to using prokaryotic cells
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Pathogenicity | Use non-pathogenic strains |
| Contamination | Use sterile techniques |
| Growth rate | Optimize growth conditions |
| Metabolic activity | Engineer cells to produce desired products |
Conclusion
Prokaryotic cells are a diverse group of organisms that play a vital role in the environment and in human health. They are the simplest and oldest type of cell, and they are found in a wide variety of habitats. Prokaryotic cells are responsible for a wide range of processes, such as decomposition, fermentation, and nitrogen fixation. They are also used in a variety of applications, such as food production, medicine, and bioremediation.