In the intricate tapestry of international relations, supranational organizations loom as influential actors, transcending national boundaries to shape global affairs. These entities wield immense power, fostering cooperation, promoting economic integration, and addressing transnational challenges. For students of AP Human Geography, understanding the nature and significance of supranational organizations is paramount.

Defining Supranational Organizations
Supranational organizations are intergovernmental entities established by treaty among member states. They possess a degree of autonomy from individual governments and are empowered to make decisions binding on their members. Unlike international organizations, which facilitate dialogue and cooperation without binding authority, supranational organizations exercise real power over specific policy areas.
Types of Supranational Organizations
The landscape of supranational organizations is diverse, encompassing a wide range of entities with varying mandates and structures. Some of the most prominent types include:
- Political organizations: Promote political cooperation and security, such as the United Nations (UN) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
- Economic organizations: Facilitate economic integration and trade, such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Social and cultural organizations: Foster cooperation in areas such as education, health, and human rights, such as the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
Key Characteristics of Supranational Organizations
- Treaty-based: Established through agreements ratified by member states.
- Autonomy: Possess a degree of independence from individual governments.
- Decision-making power: Can make decisions that are binding on members.
- Member states: Consists of sovereign states that have voluntarily joined.
- Institutional structure: Typically includes legislative, executive, and judicial bodies.
Importance of Supranational Organizations
Supranational organizations play a crucial role in global affairs, performing a multitude of vital functions:
- Facilitating cooperation: Provide a platform for member states to collaborate on issues of shared interest.
- Promoting economic growth: Facilitate trade, investment, and development through economic integration.
- Addressing transnational challenges: Coordinate responses to global issues such as climate change, poverty, and terrorism.
- Maintaining peace and security: Promote cooperation on defense and security matters, preventing conflict and maintaining stability.
- Protecting human rights: Establish and enforce international norms for the protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms.
Examples of Supranational Organizations
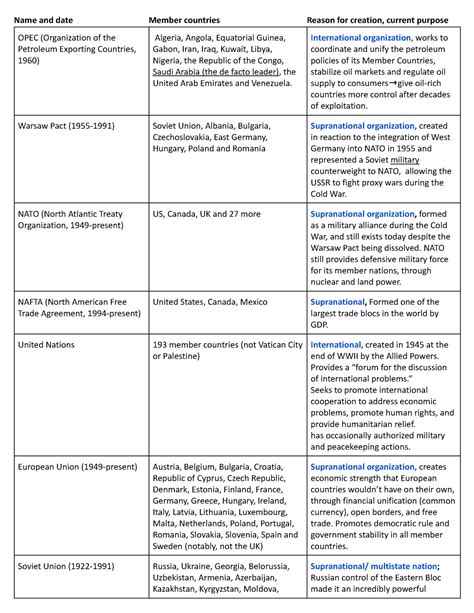
- United Nations (UN): A global intergovernmental organization with 193 member states, addressing issues such as peace, security, human rights, and development.
- World Trade Organization (WTO): Facilitates global trade by establishing rules and regulations for international commerce.
- European Union (EU): A political and economic union of 27 member states in Europe, promoting economic integration and cooperation.
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN): A political and economic organization of 10 Southeast Asian countries, promoting regional cooperation and integration.
- African Union (AU): A political and economic union of 55 African countries, promoting peace, security, and development on the continent.
Data on Supranational Organizations
According to the United Nations, there are over 500 intergovernmental organizations in the world. The vast majority of these organizations are supranational in nature, with varying degrees of autonomy and decision-making power. The following table provides data on some of the largest supranational organizations:
| Organization | Founded | Headquarters | Member States |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Nations | 1945 | New York City | 193 |
| European Union | 1957 | Brussels | 27 |
| World Trade Organization | 1995 | Geneva | 164 |
| Association of Southeast Asian Nations | 1967 | Jakarta | 10 |
| African Union | 2002 | Addis Ababa | 55 |
Supranational Organizations in AP Human Geography
In the AP Human Geography curriculum, supranational organizations are a key component of the study of globalization. Students are expected to understand the different types of supranational organizations, their functions, and their impact on the world. Specific examples of supranational organizations are often used to illustrate concepts such as economic integration, political cooperation, and the interconnectedness of the global system.
Tips and Tricks for Studying Supranational Organizations
To excel in your study of supranational organizations, consider the following tips:
- Understand the different types: Familiarize yourself with the various categories of supranational organizations, including political, economic, and social organizations.
- Identify key characteristics: Remember the defining features of supranational organizations, such as their treaty-based nature, autonomy, and decision-making power.
- Analyze their functions: Understand the specific roles played by supranational organizations in facilitating cooperation, promoting economic growth, and addressing transnational challenges.
- Compare and contrast examples: Study examples of supranational organizations such as the UN, EU, and WTO to gain a deeper understanding of their specific mandates and operations.
- Use visuals: Utilize maps, charts, and diagrams to visualize the distribution and connections between supranational organizations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To prevent common pitfalls, avoid these mistakes:
- Confusing supranational organizations with international organizations: Remember that supranational organizations possess binding authority, while international organizations have no such power.
- Oversimplifying their functions: Supranational organizations perform a complex and nuanced range of functions, beyond mere cooperation or economic integration.
- Ignoring their limitations: Supranational organizations are not always effective or universally accepted, facing challenges such as bureaucratic complexity and political resistance.
- Failing to appreciate their interconnectedness: Supranational organizations often work together and interact with each other, forming a complex global network.
- Underestimating their impact: The influence of supranational organizations is far-reaching, shaping the political, economic, and social landscapes of the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a supranational organization and an intergovernmental organization?
A: Supranational organizations are a type of intergovernmental organization that possesses decision-making power, while other intergovernmental organizations do not.
Q: What are the advantages of supranational organizations?
A: Supranational organizations facilitate cooperation, promote economic growth, address transnational challenges, maintain peace and security, and protect human rights.
Q: What are the challenges faced by supranational organizations?
A: Supranational organizations face challenges such as bureaucratic complexity, political resistance, and the need for consensus among member states.
Q: How can I stay updated on the latest developments in supranational organizations?
A: Follow news outlets, read academic journals, and visit the official websites of supranational organizations for up-to-date information.
Q: What are the future prospects for supranational organizations?
A: The future of supranational organizations is uncertain, with some commentators predicting increased cooperation and integration, while others foresee potential challenges from nationalism and globalization.
Q: How can I get involved with supranational organizations?
A: Consider working for supranational organizations, volunteering with their affiliated NGOs, or participating in their educational programs and initiatives.
Conclusion
Supranational organizations are indispensable actors on the global stage, shaping the course of international affairs and addressing transnational challenges that transcend national boundaries. By understanding the nature, functions, and significance of supranational organizations, students of AP Human Geography gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of global interconnectedness and the role of these powerful entities in shaping our world.