Introduction
Navigate the turbulent waters of APUSH Period 3 with the ultimate guide, our comprehensive APUSH Period 3 Quizlet. This digital treasure trove will illuminate the pivotal events that shaped the United States in the tumultuous era of revolution and westward expansion.

Key Concepts
- American Revolution (1775-1783): The colonists’ struggle for independence from British rule
- Articles of Confederation: The first framework for governing the United States
- Constitution of 1787: The enduring foundation of the American government
- Louisiana Purchase (1803): The acquisition of vast lands from France, doubling the size of the US
- War of 1812: The second war of independence against Great Britain
Vocabulary
- Tariff: A tax on imported goods
- Embargo: A ban on trade with other countries
- Manifest Destiny: The belief that the US had a divine right to expand westward
- Nullification: The idea that states had the right to reject federal laws
- Secession: The act of withdrawing from the Union
Historical Figures
- George Washington: Commander-in-chief of the Continental Army and first President of the US
- Thomas Jefferson: Author of the Declaration of Independence and third President of the US
- Benjamin Franklin: Inventor, diplomat, and Founding Father
- Napoleon Bonaparte: Emperor of France who sold the Louisiana Territory to the US
- Andrew Jackson: Seventh President of the US and a key figure in westward expansion
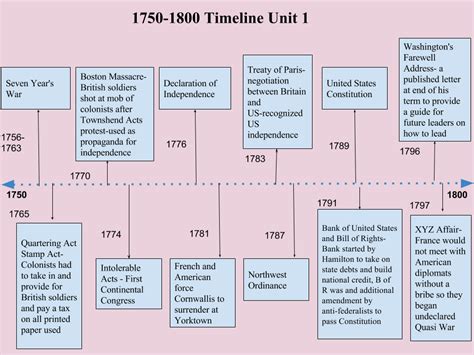
Timeline
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1775 | Battle of Lexington and Concord begins the American Revolution |
| 1776 | Declaration of Independence adopted |
| 1781 | Battle of Yorktown ends the American Revolution |
| 1787 | Constitutional Convention drafts the Constitution |
| 1803 | Louisiana Purchase |
| 1812 | War of 1812 begins |
| 1815 | Battle of New Orleans ends the War of 1812 |
Key Battles
- Battle of Saratoga (1777): Turning point in the American Revolution
- Battle of Yorktown (1781): Final major battle of the American Revolution
- Battle of New Orleans (1815): Andrew Jackson’s victory that ended the War of 1812
Cause and Effect
Causes of the American Revolution
- British taxation without representation
- Restrictions on colonists’ rights
- Desire for self-government
Effects of the American Revolution
- Independence from Great Britain
- Establishment of a new nation, the United States of America
- Spread of republican ideals throughout the world
Impact of Westward Expansion
- Acquisition of vast new territories
- Growth of the nation’s size and power
- Displacement of Native American tribes
- Development of new industries and economies
Tables
Table 1: Important Documents
| Document | Year | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration of Independence | 1776 | Declared the colonies’ independence from Great Britain |
| Articles of Confederation | 1781 | First framework for governing the US |
| Constitution of 1787 | 1788 | Established the enduring foundation of the American government |
Table 2: Key Battles of the American Revolution
| Battle | Date | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of Lexington and Concord | 1775 | Began the American Revolution |
| Battle of Saratoga | 1777 | Turning point in the American Revolution |
| Battle of Yorktown | 1781 | Ended the American Revolution |
Table 3: Causes and Effects of the War of 1812
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| British impressment of American sailors | Second war of independence against Great Britain |
| British support for Native American attacks on American settlements | Strengthening of American national identity |
| American desire to expand westward | Acquisition of new territories |
Table 4: Key Figures of APUSH Period 3
| Figure | Role |
|---|---|
| George Washington | Commander-in-chief of the Continental Army, first President of the US |
| Thomas Jefferson | Author of the Declaration of Independence, third President of the US |
| Benjamin Franklin | Inventor, diplomat, Founding Father |
| Napoleon Bonaparte | Emperor of France, sold the Louisiana Territory to the US |
| Andrew Jackson | Seventh President of the US, key figure in westward expansion |
Effective Strategies
- Break down the material into smaller chunks: Study the quizlet terms in smaller groups, focusing on one concept or event at a time.
- Use active recall: Regularly test yourself on the material, trying to recall the terms and definitions without looking at the answer.
- Spaced repetition: Review the material at increasing intervals (e.g., 1 day, 3 days, 7 days) to strengthen your retention.
- Create your own study materials: Summarize the key points in your own words, make flashcards, or draw diagrams to enhance your understanding.
Tips and Tricks
- Use the “Learn” function: The quizlet app offers a variety of study modes, including the “Learn” mode which uses flashcards and other interactive exercises.
- Join a study group: Collaborating with other students can improve your comprehension and motivation.
- Use the “Share” feature: Share your quizlet sets with classmates or friends to help them study.
- Take advantage of the “Classic” mode: The “Classic” mode offers a more traditional quiz format with multiple-choice questions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Cramming at the last minute: Give yourself ample time to study the material and avoid cramming the night before the test.
- Relying solely on memory: Use active recall techniques to strengthen your retention instead of relying on passive memorization.
- Ignoring the context: Understand the historical context of the events and terms you are studying to deepen your comprehension.
- Neglecting the “Wild Card” terms: The quizlet app generates “Wild Card” terms that are not included in the main set. Make sure to review these terms as well.