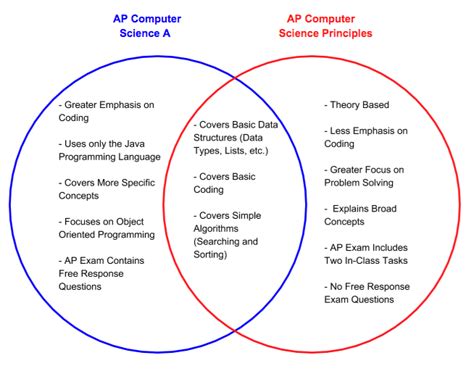
Section 1: Computing Principles and Practices
1.1 Abstraction and Modularity

- Define abstraction as the process of removing unnecessary details.
- Explain the benefits of modularity, such as code reuse and maintenance.
- Practice identifying abstract data types (ADTs) and implementing them using objects.
1.2 Data Representation and Manipulation
- Understand various data structures, including lists, stacks, queues, and trees.
- Implement basic data manipulation operations, such as sorting, searching, and inserting.
- Analyze the efficiency of different data structures for specific tasks.
Section 2: Problem Solving and Program Design
2.1 Algorithms and Problem Solving
- Define an algorithm as a set of instructions for solving a problem.
- Analyze the time and space complexity of common algorithms.
- Practice developing and implementing algorithms for various problems.
2.2 Program Design Patterns
- Explain the purpose and benefits of using design patterns.
- Identify common design patterns, such as Model-View-Controller (MVC) and Singleton.
- Apply design patterns to improve the organization and maintainability of code.
2.3 Software Development Process
- Describe the stages of software development, including requirements gathering, design, implementation, and testing.
- Understand the importance of version control and documentation.
- Practice using software development tools, such as IDEs and debuggers.
Section 3: Object-Oriented Programming
3.1 Object-Oriented Concepts
- Define the key principles of object-oriented programming (OOP), such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Understand the difference between classes and objects.
- Practice creating and using objects to represent real-world entities.
3.2 Inheritance and Interfaces
- Explain the concept of inheritance and how it allows classes to reuse and extend functionality.
- Implement inheritance hierarchies and override methods to create polymorphic behavior.
- Define and use interfaces to specify contracts between classes.
3.3 Exception Handling
- Understand the importance of exception handling for managing errors.
- Implement custom exception classes to handle specific types of errors.
- Practice using try-catch blocks to handle exceptions and provide meaningful error messages.
Section 4: Database Concepts
4.1 Relational Databases
- Define the structure of a relational database and its components (tables, rows, columns).
- Perform basic SQL queries to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data.
- Understand the principles of data normalization and its benefits.
4.2 Data Integrity and Security
- Explain the importance of data integrity and the techniques used to ensure it, such as primary keys and foreign keys.
- Understand the different types of security threats and the measures used to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Implement basic data security measures, such as encryption and access control.
Section 5: Cybersecurity Concepts
5.1 Cybersecurity Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Identify common cybersecurity threats, such as malware, viruses, and phishing attempts.
- Understand the different types of vulnerabilities that can expose systems to attacks.
- Describe the techniques used to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access.
5.2 Cybersecurity Defenses
- Explain the importance of strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Describe the role of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security technologies in protecting networks.
- Practice implementing basic cybersecurity measures to protect user data and systems.
Section 6: Ethical and Social Issues
6.1 Ethical Considerations
- Discuss the ethical implications of computing, such as privacy, data security, and intellectual property rights.
- Understand the responsibilities of software developers and users in maintaining ethical practices.
- Explain the importance of following ethical guidelines and codes of conduct.
6.2 Social Impact
- Examine the positive and negative social impacts of computing technology.
- Discuss the role of computing in transforming industries, improving communication, and addressing global challenges.
- Explore the potential ethical, social, and environmental considerations associated with emerging technologies.
Study Guide Tips
Tips:
- Start early and study consistently throughout the course.
- Attend all class sessions and actively participate in discussions.
- Review lecture notes and assigned readings regularly.
- Practice coding daily to improve your programming skills.
- Use online resources and tutorials to supplement your learning.
- Form study groups with classmates to collaborate and review material.
- Take practice exams and mock tests to gauge your understanding.
- Seek assistance from the teacher or a tutor if needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Underestimating the importance of abstraction and modularity.
- Neglecting to practice algorithm development and analysis.
- Failing to master the basics of OOP, such as inheritance and polymorphism.
- Overlooking the significance of database normalization and security.
- Ignoring cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Underestimating the ethical implications of computing technology.
Generating Creative New Applications
“Computrize” a word or phrase (add “compu” to the beginning) to generate ideas for new applications:
| Computrized Word | New Application Idea |
|---|---|
| CompuDraw | Software for creating and editing diagrams |
| CompuOrganize | Task management and organization platform |
| CompuFit | Fitness tracking and workout planner |
| CompuBudget | Financial planning and budgeting app |
| CompuMed | Healthcare data management and analytics system |
Useful Tables
Table 1: Data Structure Characteristics
| Data Structure | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| List | O(n) | O(n) |
| Stack | O(1) | O(n) |
| Queue | O(1) | O(n) |
| Tree | O(log n) | O(n) |
Table 2: Cybersecurity Threats and Countermeasures
| Threat | Countermeasure |
|---|---|
| Malware | Antivirus software |
| Phishing | Anti-phishing filters |
| Denial of Service (DoS) | Firewalls, rate limiting |
| Data Breach | Encryption, access control |
| Social Engineering | User awareness training |
Table 3: Ethical Considerations in Computing
| Issue | Ethical Principle |
|---|---|
| Privacy | Protect user data from unauthorized access |
| Intellectual Property | Respect copyright laws and attribution |
| Bias | Avoid creating biased or discriminatory algorithms |
| Accountability | Hold developers and users responsible for the consequences of their actions |
| Transparency | Disclose information about how computing systems work and use data |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid in AP CSP
| Mistake | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Ignoring abstraction | Code becomes difficult to understand and maintain |
| Neglecting algorithm analysis | Poorly performing algorithms can lead to inefficient programs |
| Misusing inheritance | Unintended behavior or code duplication can occur |
| Overlooking SQL fundamentals | Difficulty in retrieving and manipulating data |
| Underestimating cybersecurity risks | Systems become vulnerable to attacks |